FIG 2, A-E.

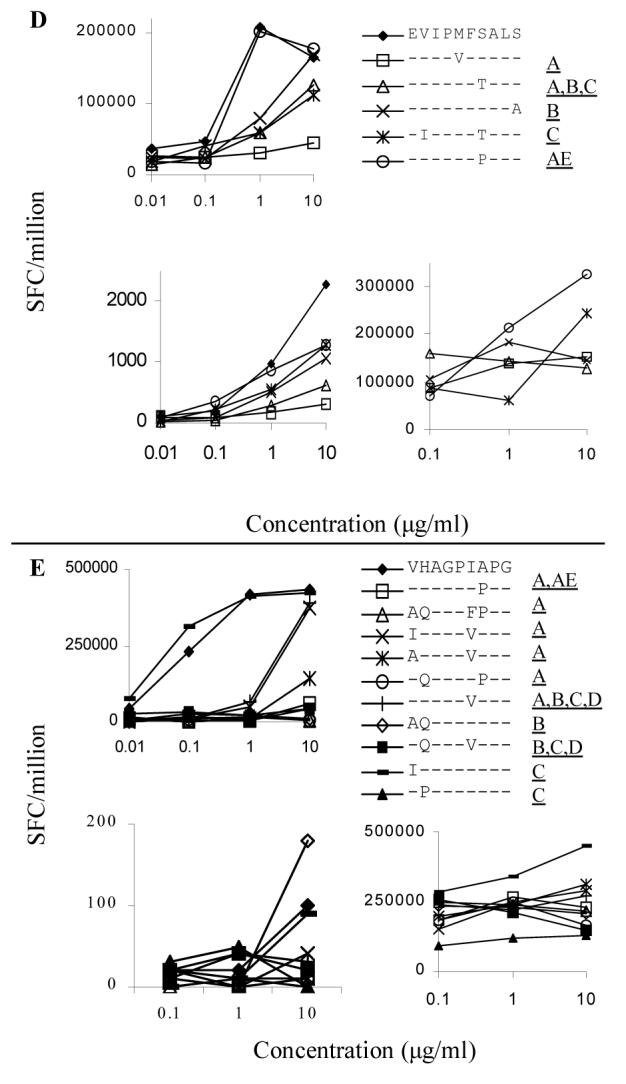
Upper left panels: Clonal response to cross-clade peptides. IFN-γ secretion was measured by ELISPOT over a range of peptide concentrations from 0.1 to 10 μg/ml. The clone used to analyze each epitope is listed in Table 1. The clade B consensus peptide is represented by the filled diamond (◆) for each of the epitopes. Peptides that elicit more than 50% less IFN-γ than the clade B epitope are marked in the legend with a dashed line. Clones were assayed at 100 cells per well and responses are listed as SFC/million. Each condition was performed in duplicate and these results represent the average of at least two assays performed on separate occasions.
Lower left panels: Polyclonal response to cross-clade peptides. PBMC and p24-specific T cell lines were stimulated with the same panel of peptides studied at the clonal level. Fig. 1D shows data generated with fresh PBMC, all other graphs were derived using T cell lines. The subject from whom each T cell line was derived is listed above the graph. PBMC responses were too low to consistently detect in most individuals so T cell lines were generated. Lines were restimulated 10-14 days after initial antigen-specific stimulation and were assayed 10 days later. PBMC and T cell lines were assayed at 50,000 cells/well and results are listed as SFC/million. IFN-γ secretion was about 100-fold less in the polyclonal than in the clonal response. Each condition was performed in duplicate. Background ranged from 1 to 2.5 spots per well and was not subtracted in the figures.
Lower right panels: Antagonism of clonal responses. Cross-clade peptides were unable to antagonize the clonal response to the clade B consensus peptide. The clone used to analyze each epitope is listed in Table 1. All wells included 1 μg/ml of clade B consensus peptide, except for epitope ET10 that required 10 μg/ml for activation of the clone. The variant peptides were added at increasing concentration to the wells and each condition was performed in duplicate. Clones were assayed at 100 cells/well and results represent the average of two separate experiments. No consistent inhibition of the clonal response to the clade B peptide was seen.
