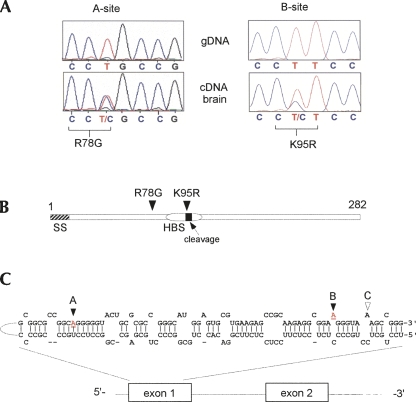
FIGURE 4.
RNA editing of IGF-binding protein 7. (A) Sequence traces obtained from amplified genomic DNA and matching cDNA samples encompassing the predicted RNA editing sites A and B within the IGFBP7 exon 1 sequence (reverse complement sequence of mRNA is shown). A double-peak of T and C indicates a mixed population of mRNAs in the cDNA samples due to post-transcriptional A-to-I RNA modification in the sense strand. (B) Schematic representation of the IGFBP7 open reading frame indicating functional domains. The positions of the two editing sites with ensuing amino acid change are depicted. SS=signal sequence consisting of amino acid residues 1–26; HBS=heparin binding site encompassing amino acids 89–97; cleavage=protease processing site at amino acid position 97. (C) Predicted (Mfold) RNA fold encompassing the IGFBP7 editing sites A and B (underlined and highlighted in red) within exon 1. Also labeled is a third potential minor editing site (C) that did not show evidence of editing in vivo according to our screening analysis and might represent a true genomic SNP.