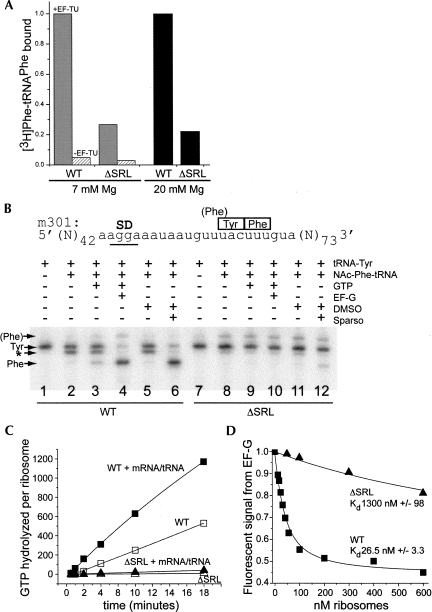
FIGURE 4.
ΔSRL 50S subunits are defective in EF-Tu-dependent and nonenzymatic A-site tRNA binding and in interaction with EF-G. (A) [3H]-Phe-tRNAPhe was bound to the A site of ribosomal complexes containing mRNA and fMet-tRNAfMet under either EF-Tu-dependent (gray and hatched bars, 7 mM Mg), or nonenzymatic (black bars, 20 mM Mg) conditions. A-site binding was normalized to the highest level obtained by WT ribosomes, which corresponds to 0.95 [3H]-Phe-tRNAPhe per ribosome (EF-Tu-dependent) and 0.8 per ribosome (nonenzymatic). (B) Toeprint analysis of tRNA binding and translocation using m301 mRNA; ribosomal complexes contain tRNA and factors as indicated. Reverse transcriptase stops (arrows) correspond to the indicated codons in the P site, and the doublet band indicates A-site-bound tRNA (*). (C) Ribosome-dependent EF-G·GTP hydrolysis. ΔSRL (triangle) or WT (square) vacant ribosomes (filled symbols) or those containing polyU mRNA and tRNAPhe (open symbols) were incubated in the presence of EF-G and [32P]-γ-GTP. (D) EF-G binding. Quenching of fluorescein-labeled EF-G was measured with increasing concentrations of ΔSRL (▲) or WT (■) ribosomal complexes containing mRNA and tRNAfMet.