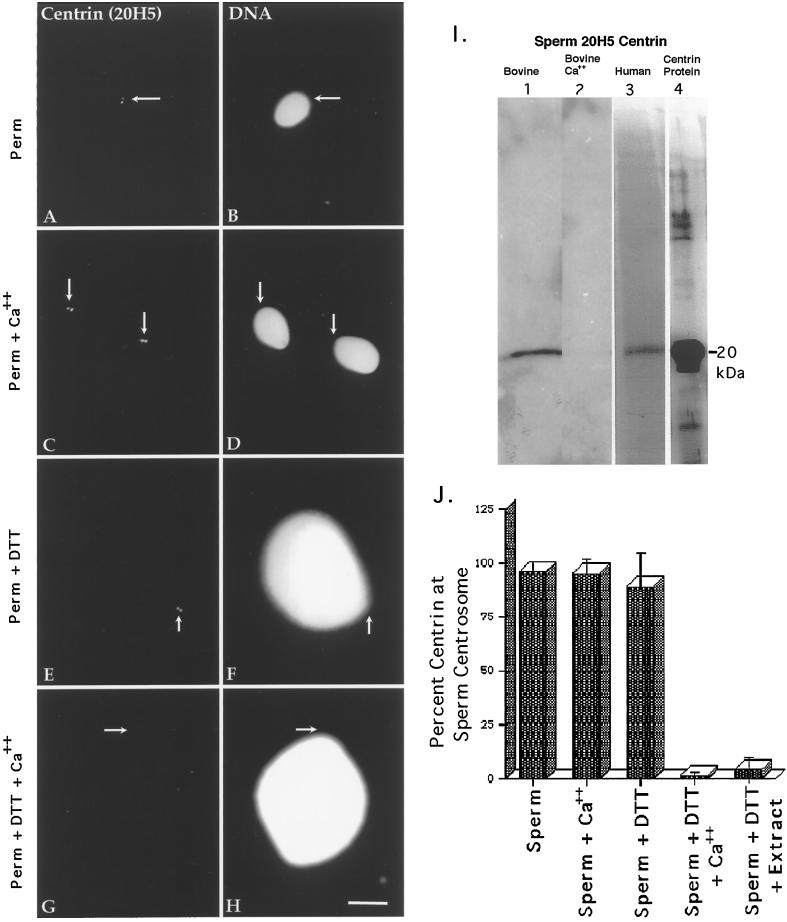
Figure 2.
Centrin in human sperm centrosomes. Centrin is localized exclusively as either a pair of punctate sources or a single spot (depending on orientation) at the centrosome in permeabilized human sperm (A, centrin antibody 20H5; B, DNA) or permeabilized spermatozoa exposed to 2 mM CaCl2 (C and D). This staining is not dependent on calcium exposure. Sperm exposed to 5 mM DTT (E and F) for 40 min show no change in the centrin-staining pattern from controls. However, spermatozoa exposed to DTT and 2 mM CaCl2 show a dissipation of centrin staining (G and H). Arrows indicate the point of tail attachment to the sperm head as observed with phase or differential interference contrast optics. Identical results were found with bovine sperm. (I) Western blots of bovine and human sperm, demonstrating a single band at ∼20 kDa that comigrates with bacterially expressed centrin and the calcium sensitivity of sperm centrosomal centrin. Lane 1, DTT-primed bovine sperm (60 μg of total protein per lane); lane 2, DTT-primed bovine sperm treated for 30 min with 2 mM CaCl2, showing the loss in 20H5 centrin detection after high external calcium treatment (43 μg of total protein per lane); lane 3, human sperm, immunoprecipitated with 20H5 anti-centrin and immunostained with anti-centrin serum 24/14-1; lane 4, purified bacterially expressed centrin protein immunostained with anti-centrin serum 24/14-1. (J). Graphic representation of human spermatozoa immunostained with 20H5 centrin after permeabilization, DTT priming, and elevated external calcium exposure. Analysis reveals that DTT-primed spermatozoa treated with either high external calcium (fourth bar) or CSF-arrested extract (fifth bar) demonstrate a significant reduction in the detection of centrin at the sperm centrosome. Bar in H, 10 μm.