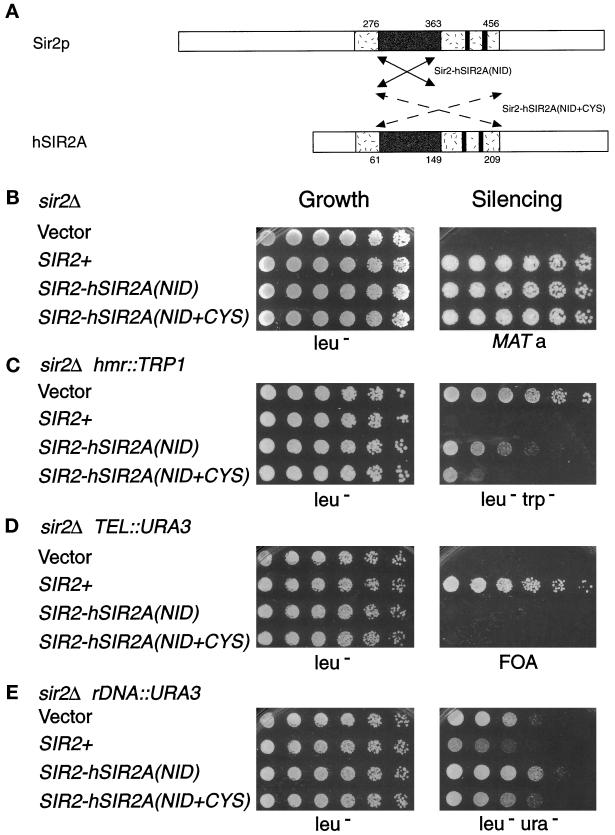
Figure 4.
The Sir2-hSir2A chimeras function in transcriptional silencing. (A) The arrows denote the region of the human Sir2A core exchanged for that of the Sir2p core in the Sir2-hSir2A(NID) chimera (solid lines indicate aa 276–363 of Sir2p were replaced with aa 61–149 of hSir2Ap) and in the Sir2-hSir2A(NID+CYS) chimera (dashed lines indicate aa 276–456 of Sir2p were replaced with aa 61–209 of hSir2Ap). (See Figure 1B for the sequences exchanged in the chimeras.) (B–E) Results of dilution assays to test the SIR2-hSIR2A(NID) (pLP999) and SIR2-hSIR2A(NID+CYS) (pLP905) chimeras’ complementation of the sir2Δ mating defect in LPY1403 (MATα sir2Δ hml:: TRP1) (B), hmr::TRP1 silencing defect in LPY3923 (MATa sir2Δ hmrΔ::TRP1) (C), telomeric silencing defect in LPY1953 (MATa sir2Δ TEL::URA3) (D), and rDNA silencing defect in LPY2447 (MATα sir2Δ rDNA::URA3) (E). The left panel depicts growth of serial dilutions on leu− plates as a control, and the right panel depicts growth on a his4 (LPY143) mating tester on minimal plates (B), leu−trp− (C), 5-FOA (D), and leu−ura− (E).