Abstract
Hitherto the laboriousness of serological procedures for the laboratory diagnosis of leptospirosis has somewhat limited their usefulness. The authors of this paper report on a simple and sensitive genus-specific serological test for this disease that is within the capabilities of ordinary diagnostic laboratories. They describe the organization and results of a trial carried out in Romania in 1962 of a complement-fixation (CF) test in leptospirosis in which an antigen derived from the Patoc I strain of Leptospira biflexa is used. Human sera examined with this test in nine field laboratories were re-examined at the Cantacuzino Institute in Bucharest with both CF and agglutination tests.
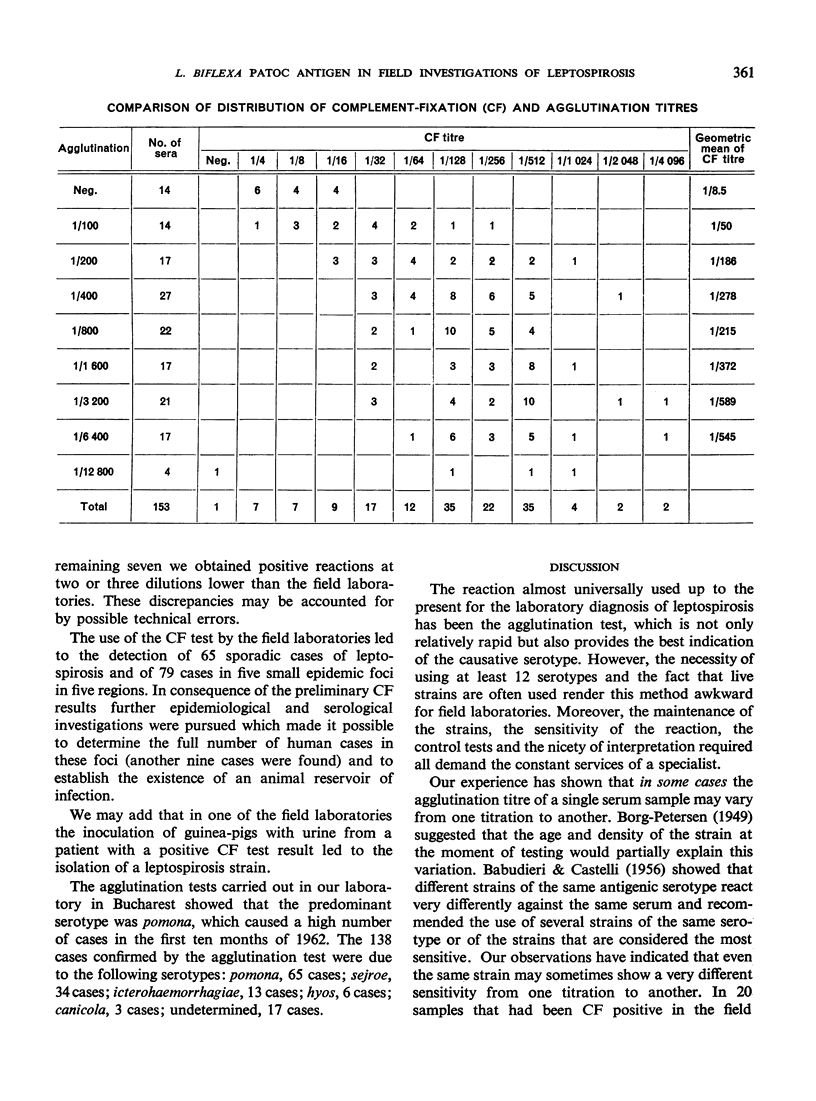
Of 152 sera found CF-positive in the field laboratories, 138 were found positive by the agglutination test in Bucharest—representing 90% agreement. There was 88% agreement between the field laboratory and central laboratory results in the CF test.
The test makes possible the early detection of human leptospirosis and gives positive reactions with sera from leptospirosis patients irrespective of the causative serotype.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COMBIESCU D., STURDZA N., SEFER M., RADU I. Leptospirenforschungen in Rumänien. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1958 Nov;173(1-2):103–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


