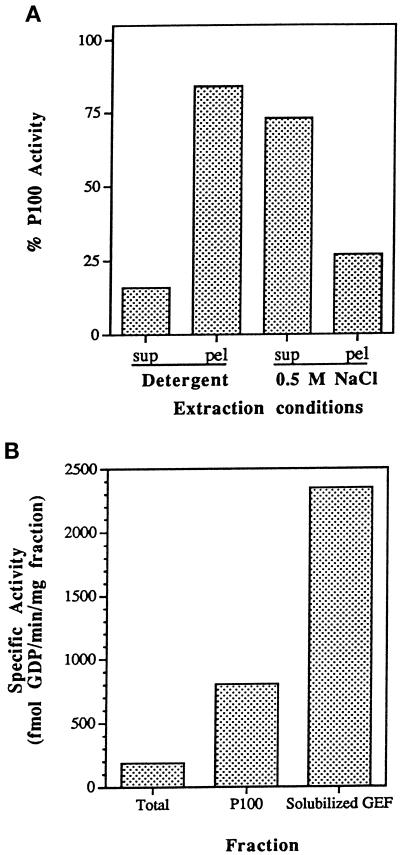
Figure 2.
Association of the Ypt1p-GEF with the P100 fraction and preparation of the solubilized GEF fraction. (A) Extraction of Ypt1p-GEF from the P100 fraction by salt but not by detergents is shown. P100 was treated with 1% Triton X-100, 30 mM n-octylglucoside, or 0.5 M NaCl. Equal volumes of the P100 fraction and the treated pellets and supernatants were diluted at least fivefold into the reaction mixture (NaCl concentrations were at or below 100 mM, a concentration that does not affect intrinsic or stimulated exchange) and were assayed for their ability to stimulate release of [3H]GDP from Ypt1p as described. Addition of 1% Triton X-100, 30 mM n-octylglucoside, or 0.5 M NaCl to the unfractionated P100 had no effect on its activity. Extracts were prepared at least twice and were assayed at least twice per extraction with equivalent results. Extraction with 1% Triton X-100 and 30 mM n-octylglucoside gave identical results and are presented as Detergent. (B) Sequential extraction of the P100 fraction with Triton X-100 and NaCl yields a soluble Ypt1p-GEF activity and an additional fourfold increase in specific activity. The solubilized GEF fraction is the S100 fraction from sequential extraction of the P100 fraction with 1% Triton X-100, followed by extraction of the resulting pellet with 0.5 M NaCl. The total enrichment of the Ypt1p-GEF activity in the solubilized fraction relative to the crude cell extract is 16- to 20-fold. Similar results were obtained with four independent preparations.