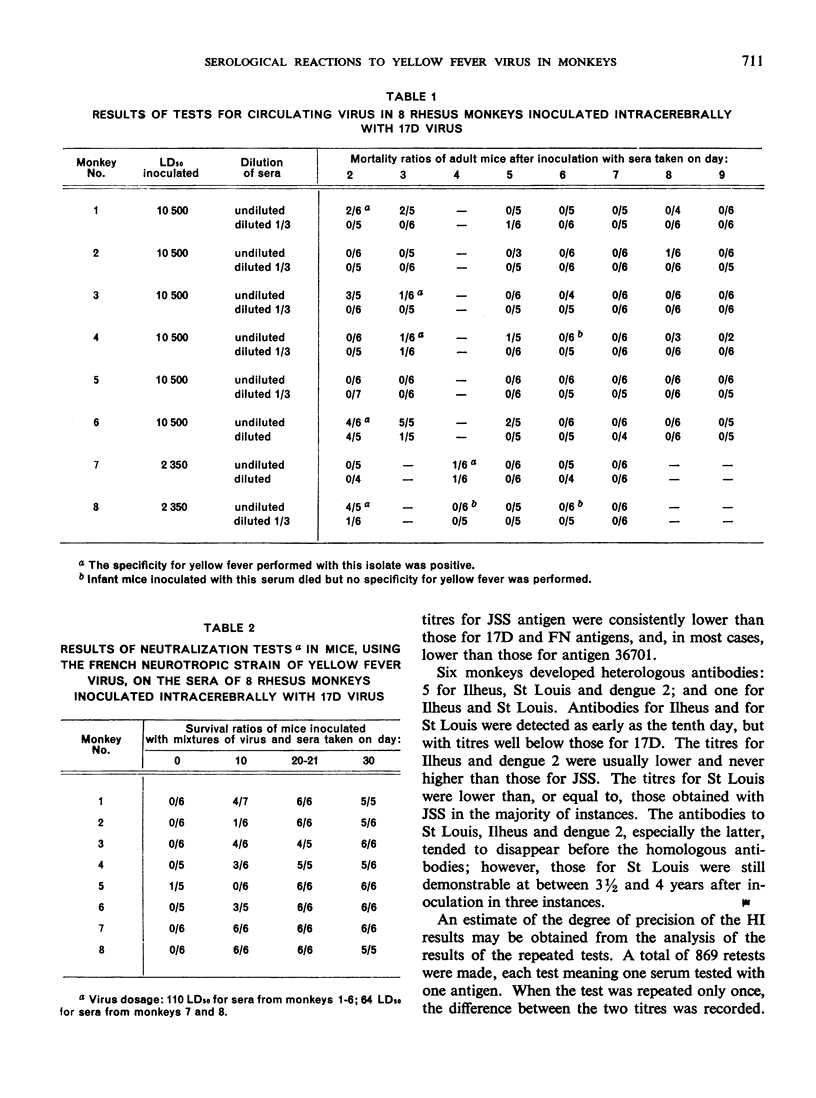
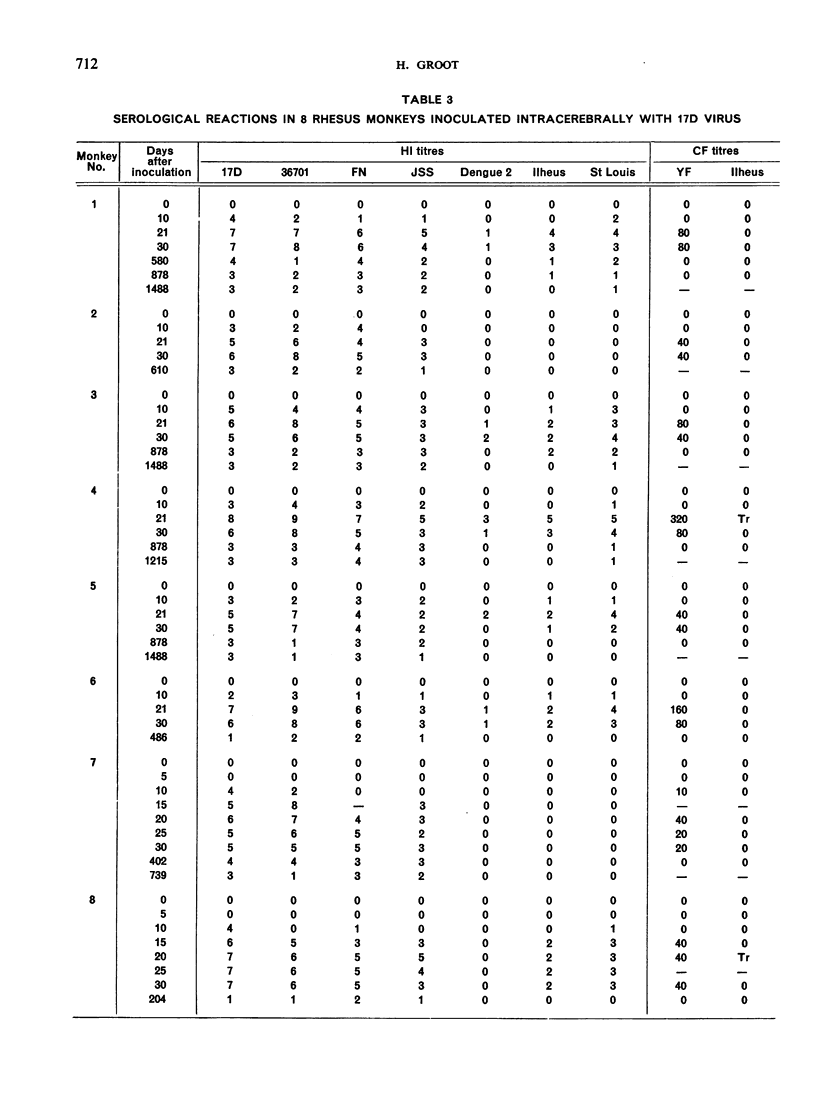
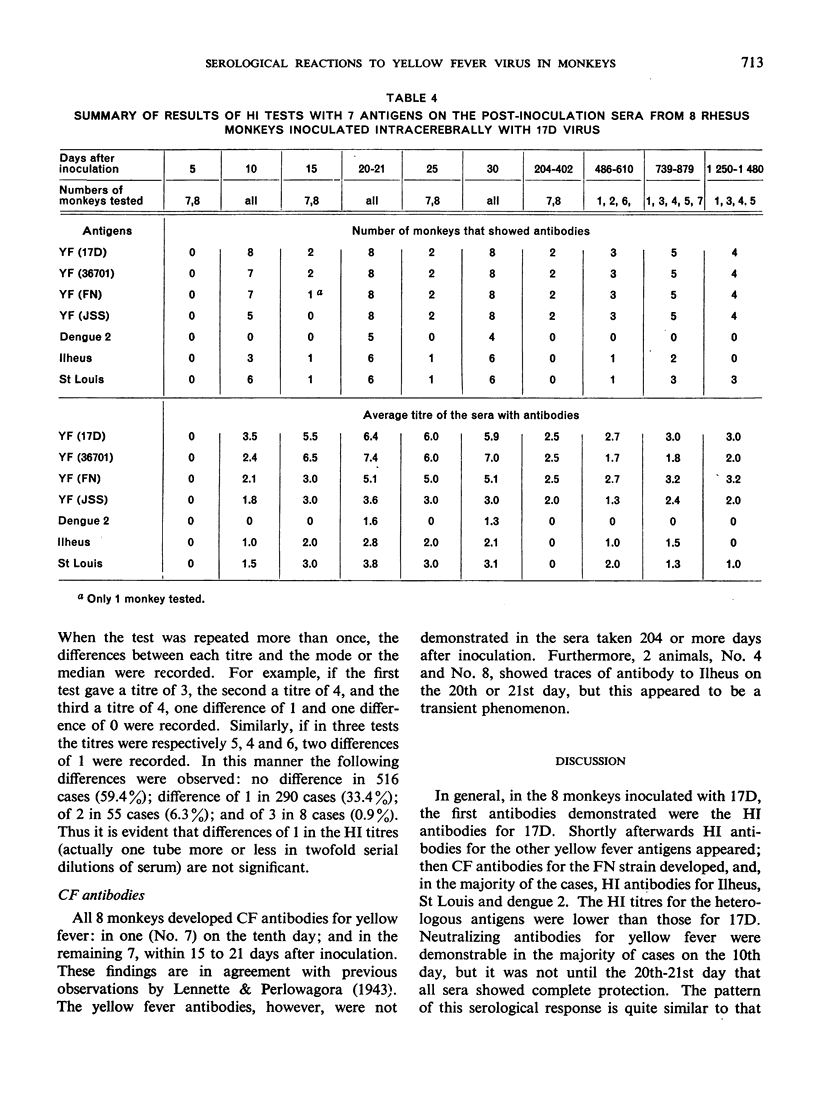
Abstract
Haemagglutination-inhibition tests, which depend on the appearance of haemagglutination-inhibiting antibodies in the serum in virus infections, are in common use in the study of arthropod-borne diseases. This paper contains the results of an investigation into the appearance and pattern of haemagglutination-inhibiting antibodies in the serum of rhesus monkeys inoculated intracerebrally with the 17D strain of yellow fever virus during the testing of seed lots of yellow fever vaccine. These antibodies appeared on the tenth day after inoculation, and were still demonstrable four years later. In all of the eight monkeys tested complement-fixing and neutralizing antibodies against yellow fever antigens also developed, and in six out of the eight heterologous antigens developed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casals J., Palacios R. THE COMPLEMENT FIXATION TEST IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF VIRUS INFECTIONS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. J Exp Med. 1941 Oct 31;74(5):409–426. doi: 10.1084/jem.74.5.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


