Abstract
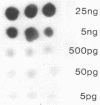
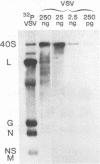
To develop a highly sensitive and direct assay for defective interfering (DI) particles of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), we reverse transcribed RNA from DI particles and cloned the DNA in pBR322 and used it as hybridization probes. At the lower limit, cDNA of about 850 nucleotides detected 150 pg of VSV RNA. For differentiation of hybridizable sequences found in the RNA of DI particles from complementary or identical sequences in the L mRNA or standard genomic RNA of VSV, RNA obtained from mouse brains was first separated by size, blotted onto nitrocellulose, and then hybridized to in vitro-labeled cDNA probe. Genomic VSV, DI, or L mRNA sequences from one-half of the brain of an infected mouse were detectable, whereas uninfected mice failed to react with this specific probe. When mice were infected intranasally with 10(8) PFU of standard VSV, most of them died between days 6 and 7, and the detection of standard genomic RNA correlated with paralysis and death. DI RNA was not detected in these mice. When mice were infected with 10(8) PFU of standard VSV together with an equivalent amount of DI particles, similar results were obtained. When fewer DI particles were inoculated together with standard virus, significant protection of mice occurred together with the detection of DI RNA. These results indicate that DI particles are protective in vivo and that the details of the virus-host interaction may resemble the cyclic growth patterns in cell cultures for standard VSV and its DI particles.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Richards J. E., Slightom J. L., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. Cloning human fetal gamma globin and mouse alpha-type globin DNA: preparation and screening of shotgun collections. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1279–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.725603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell A. L., Paskind M., Reth M., Imanishi-Kari T., Rajewsky K., Baltimore D. Heavy chain variable region contribution to the NPb family of antibodies: somatic mutation evident in a gamma 2a variable region. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):625–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burckhardt J., Telford J., Birnstiel M. L. Detection of labelled RNA species by contact hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):2963–2971. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.2963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick J., Brown F. In vivo interference in vesicular stomatitis virus infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):354–359. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.354-359.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M., Holland J. J. Prophylaxis and immunization in mice by use of virus-free defective T particles to protect against intracerebral infection by vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2105–2108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Doyle M. Attempts to detect homologous autointerference in vivo with influenza virus and vesicular stomatitis virus. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.526-531.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P. Purification of defective interfering T particles of vesicular stomatitis and rabies viruses generated in vivo in brains of newborn mice. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):438–449. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D. Defective viral particles and viral disease processes. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):325–327. doi: 10.1038/226325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Manders E. K. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. IV. Transcription by standard virus in the presence of defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):909–916. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.909-916.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S. Viral pathogenesis and molecular biology. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Dec;41(4):811–821. doi: 10.1128/br.41.4.811-821.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. L., Holland J. J. Requirements for DI particle prophylaxis against vesicular stomatitis virus infection in vivo. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jul;49(1):215–220. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-1-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palma E. L., Huang A. Cyclic production of vesicular stomatitis virus caused by defective interfering particles. J Infect Dis. 1974 Apr;129(4):402–410. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.4.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz S. G., Dal Canto M. C., Johnson T. C. Infection of the central nervous system produced by mixtures of defective-interfering particles and wild-type vesicular stomatitis virus in mice. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):59–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao D. D., Huang A. S. RNA synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. X. Transcription and replication by defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):756–765. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.756-765.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Species of ribonucleic acid found in Chinese hamster ovary cells infected with plaque-forming and defective particles. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.154-161.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal L. P., Breindl M., Holland J. J. Determination of molar ratios of vesicular stomatitis virus induced RNA species in BHK21 cells. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1663–1667. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R. Pathogenicity and immunogenicity for mice of temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):309–315. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.309-315.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]