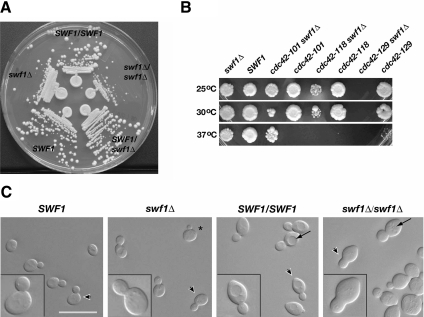
Figure 1.
Analyses of the growth, genetic interactions, and morphology of cells lacking SWF1. (A) Cells lacking SWF1 formed smaller colonies than wild-type cells. Wild-type and mutant cells were streaked on rich medium and grown for 2 d at 25°C. Shown clockwise, wild-type diploid (DDY1102), homozygous mutant (KKY 1060), heterozygous mutant (KKY1062), wild-type haploid (KKY1064), and mutant haploid (KKY1063). (B) swf1Δ displayed synthetic genetic interaction with cdc42 alleles defective in distinct processes. Equivalent dilutions of SWF1, swf1Δ, cdc42, and swf1Δ cdc42 strains were plated and grown at 25, 30, and 37°C for 2 d on rich medium. The strains shown (from left to right) are KKY1067, 281, 1070, 282, 1068, 283, and 293. No swf1Δ cdc42-129 cells were plated because these two alleles are lethal in combination. (C) Cells that lacked SWF1 had an aberrant morphology, most notably a thickening of the mother-bud neck (compare insets). Shown from left to right are differential interference-contrast images of log-phase congenic haploid wild-type (KKY1064) and swf1Δ cells (KKY1063) as well as diploid wild-type (DDY1102) and swf1Δ/swf1Δ cells (KKY1060) grown in rich medium at 25°C. Arrowheads indicate the cells presented in the insets at an enlarged view. Arrows indicate vacuoles. Bar, 10 μm.