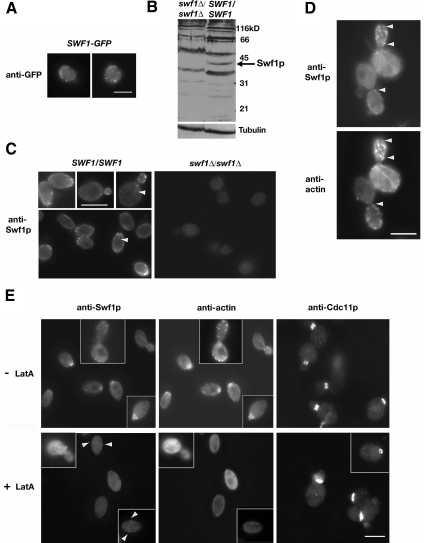
Figure 4.
Swf1p colocalized with cortical actin patches. (A) Indirect immunofluorescence micrographs of log phase wild-type cells expressing SWF1-GFP (KKY1104) labeled with anti-GFP and goat anti-rabbit-FITC antibodies. (B) Immunoblot of whole cell extract of log phase mutant swf1Δ/swf1Δ (KKY1060; right) and wild-type SWF1/SWF1 (DDY1102) diploid cells, grown at 25°C in rich medium, and probed with a polyclonal antibody against the C terminus of Swf1p. To demonstrate equivalent loading, the same blot was probed with an antibody against β-tubulin. (C) Indirect immunofluorescence micrographs of log phase wild-type SWF1/SWF1 (DDY1102; left) and mutant swf1Δ/swf1Δ (KKY1060; right) diploid cells, grown at 25°C in rich medium, and labeled with the same anti-Swf1p antibody used in B and goat anti-rabbit-Alexa 568. Arrowheads mark filamentous structures detected by the Swf1p antibody. (D) Indirect immunofluorescence micrographs of log phase wild-type cells (DDY1102) double labeled with polyclonal antibodies against Swf1p and actin. Goat anti-rabbit FITC and donkey anti-guinea pig-rhodamine served as secondary antibodies. Arrowheads mark examples of Swf1p and actin colocalization. (E) Indirect immunofluorescence micrographs of log phase wild-type SWF1/SWF1 (DDY1102; left) diploid cells cultured at 25°C in rich medium for 10 min with (bottom row) and without (top row) 400 μM LatA. The left and middle panels in each row show the same cells double labeled as in D. Arrowheads in bottom left panel mark examples of Swf1p localization. The panels on the right show cells from the same culture, with and without LatA, probed with anti-septin (Cdc11p) and goat anti-rabbit-Alexa 568 antibodies. Bars, 5 μm.