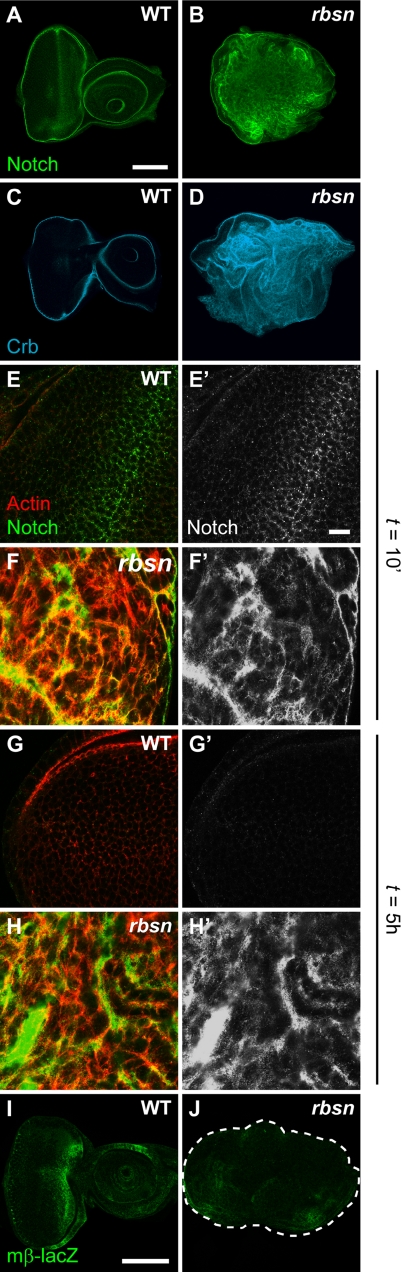
Figure 2.
Rbsn is required for uptake of endocytic cargo. The apical transmembrane proteins Notch (green; A and B) and Crumbs (Crb; cyan; C and D) are present at higher levels in rbsn discs (B and D) than in WT discs (A and C). (E–H′): Notch trafficking assays performed in WT (E and G) and rbsn (F and H) discs. Actin staining outlines cells (E–H; red). In WT cells, surface-labeled Notch (green) is found in internal puncta after 10 min (E′), and is gone from discs after 5 h (G′). In rbsn cells, Notch staining is elevated and retained at the cell periphery after 10 min (F′) and persists over the 5-h experiment (H′). The Notch signaling reporter, mβ-LacZ (I–J; green) is not ectopically activated compared with wild-type (I) in rbsn (J) mutant discs. Images shown are single confocal cross sections. Bars, 100 μm (A–D, I–J) and 10 μm (E′–H′).