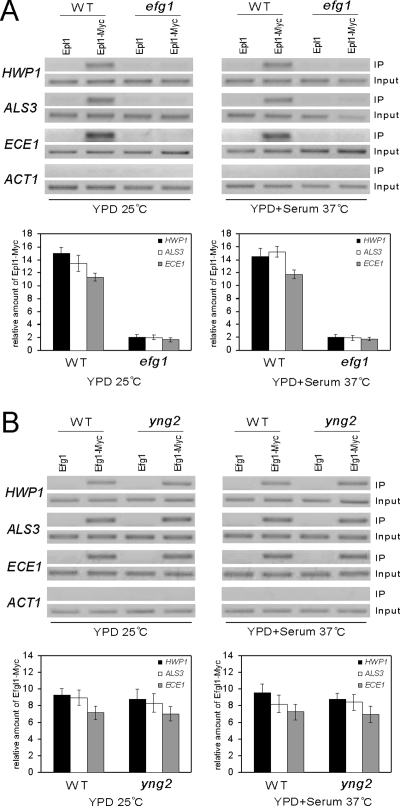
Figure 4.
Recruitment of NuA4 to promoters of hypha-specific genes is Efg1 dependent. (A) Efg1 is essential for NuA4 binding. ChIP of Epl1-myc in wild-type (CAI4) or efg1/efg1 (HLC54) strains. Cells were grown at 25°C in YPD for yeast growth and at 37°C in YPD + 10% serum for hyphal growth. PCR reactions with primers at −1381 to −1101 of HWP1, −424 to −290 of ALS3, −1350 to −1103 of ECE1, and −301 to +12 of ACT1 are shown. ChIP signals were also quantified by real-time PCR. The ADE2 promoter was used as control locus. Epl1-Myc expressing strains were used with nontagged strains as controls. HWP1, ALS3, ECE1, and control locus IP signals (bound/input) in the nontagged strains were subtracted from the values in the Myc-tagged strains. The Epl1-Myc enrichment is then presented as a ratio of HWP1, ALS3, or ECE1 IP versus control locus IP. (B) Efg1 binds the promoters of hypha-specific genes independently of Yng2. ChIP of Efg1-myc in wild-type (CAI4) or yng2/yng2 (CLY4) strains. Cells were grown at 25°C in YPD for yeast growth and at 37°C in YPD + 10% serum for hyphal growth. PCR reactions with primers at −1381 to −1101 of HWP1, −424 to −290 of ALS3, −1350 to −1103 of ECE1 are shown. For qPCR, the ADE2 promoter was used as control locus. IP ratios were calculated and are presented in A.