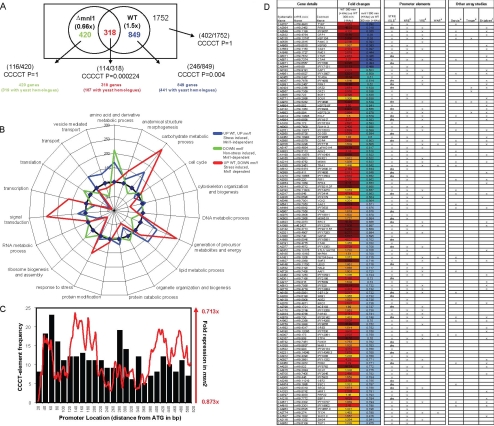
Figure 3.
Global analysis of C. albicans gene expression during exposure to weak acid stress. (A) Venn diagram showing the overlap between gene sets that are up-regulated after 300-min exposure to 20 mM acetic acid in wild-type CAI8 cells (relative to untreated cells) and those that are down-regulated in acetic acid–treated mnl1 cells (relative to acetic acid–treated wild-type cells). Numbers of genes containing STRE-like elements (CCCCT) are shown (numbers in brackets show CCCCT-containing genes/total number of genes in subset). p values indicate the chance, according to the hypergeometric probability distribution, of each sequence element occurring in each gene list compared with its overall frequency in noncoding regions of the genome. The 114 genes in the overlapping set that have a STRE-like element in the first 500 base pairs of their promoter are classed as Mnl1-dependent weak acid–responsive genes. (B) Radial plot showing frequency of GO-terms relative to all GO-terms associated with the arrayed genes with S. cerevisiae homologues. The categories shown cover the top 75% of all biological processes present in any one of the treatments. For example, genes involved with “Signal Transduction” are significantly overrepresented in the subset of genes that are induced in response to weak acid in an Mnl1-dependent manner. (C) Graph showing distribution of SLEs among promoters of Mnl1-regulated genes (■) and the mean fold difference in expression for these genes in mnl1 compared with wild-type cells (solid line indicating running average of expression for 20-base pair windows). (D) Mnl1-regulated genes showing those that contain STRE/SLE (1), NRE (2), YRE (3), or WAR elements (4). Also shown are genes (5) found to be regulated by Nrg1 in the study of García-Sánchez et al. (2005) (6), Treger's list of S. cerevisiae Msn2-regulated STRE containing genes (Treger et al., 1998), and (7) genes significantly altered under oxidative, heat shock, heavy metal, or osmotic stress; see Supplementary Material for a full list of genes.