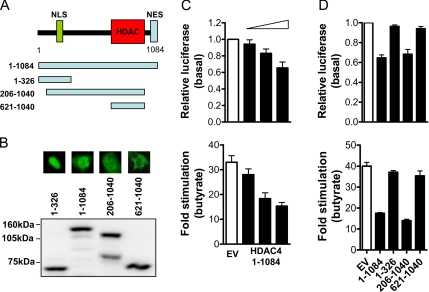
Figure 7.
HDAC4 regulation of p21 promoter activity in colon cancer cells. (A) Schematic representation of the HDAC4 protein, showing the NLS, NES, and HDAC catalytic domain. (B) Expression of the full-length and deletion HDAC4 GFP-tagged constructs (all 1 μg) in HCT116 cells was determined by anti-GFP Western blot. Also shown are immunofluorescence photomicrographs of the localization of the various HDAC4-GFP deletion mutants used. (C) Effect of HDAC4 overexpression on basal or 2 mM butyrate-induced p21 promoter activity after 24 h. HCT116 cells were cotransfected with pWP-133 (0.25 μg), TK-Renilla (0.1 μg), and increasing concentrations of HDAC4-GFP (1-1084) or the empty vector control (0–1 μg). Values shown are mean + SEM, and they are expressed as a percentage of pWP-133 activity relative to appropriate empty vector controls (empty bars) for basal p21 activity, and as -fold stimulation of p21 promoter activity for butyrate induction. (D) Effect of the HDAC4-GFP deletion constructs on basal or 2 mM butyrate-induced (24-h) p21 promoter activity. HCT116 cells were cotransfected with pWP-133 (0.25 μg), TK-Renilla (0.1 μg), and 1 μg of the HDAC4-GFP full-length and deletion constructs, or the empty vector control (1 μg). Values shown are mean + SEM, and they are expressed as a percentage of pWP-133 activity relative to corresponding empty vector controls (empty bars) for basal p21 activity, and as -fold stimulation of p21 promoter activity for butyrate induction.