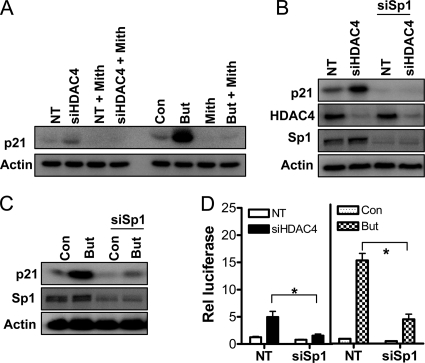
Figure 9.
Role of Sp1 in HDAC4-mediated repression of p21. (A) Effect of the Sp1 inhibitor mithramycin on siHDAC4 and butyrate-mediated p21 induction. p21 protein levels in HCT116 cells treated with mithramycin (1 μg/ml) for 24 h in combination with either a 72-h exposure to NT siRNA or siHDAC4 (100 μM), or a 24-h exposure to 2 mM butyrate. The effect of down-regulation of Sp1 on induction of p21 by siHDAC4 or butyrate is shown in B and C, respectively. p21, HDAC4, and Sp1 protein levels in HCT116 cells were determined after 72-h treatment with NT siRNA or siHDAC4 with or without concomitant treatment with siRNA targeting Sp1. All cells were treated with an equal final concentration of siRNA (100 nM). (D) Effect of Sp1 down-regulation on p21 promoter activity stimulated by siHDAC4 or butyrate, as determined by luciferase assay. HCT116 cells were transfected with pWP-133 (0.25 μg) and either NT siRNA siHDAC4 or siSp1 (total siRNA transfected was 100 nM), and cultured for 72h. In separate experiments, cells were transfected with pWP-133 (0.25 μg) and either NT siRNA or siSp1 (both 100 nM), and they were cultured with and without 2 mM butyrate for 24 h. TK-Renilla (0.1 μg) was cotransfected in all treatment groups to control for transfection efficiency. Values shown are mean + SEM of three independent experiments; *p < 0.05, Student's t test.