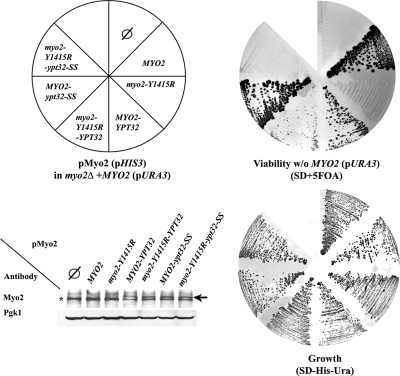
Figure 6.
Interaction between Myo2 and Ypt32 is required for yeast cell viability. Fusion with Ypt32 suppresses the lethality caused by the myo2-Y1415R mutation. Cells carrying a deletion of MYO2 on the chromosome and a URA3 plasmid expressing wild type Myo2 (YCp50-MYO2; LWY2947) were transformed with HIS3 plasmids (pRS413) expressing Myo2 from the following vectors: empty vector (∅), MYO2, myo2-Y1415R, MYO2-YPT32, myo2-Y1415R-YPT32, MYO2-ypt32-SS, and myo2-Y1415E-ypt32-SS (schematic presentation of the plate, top, left). All strains can grow on SD-His-Ura plates (bottom, right). Cells expressing wild-type Myo2 proteins—Myo2, Myo2-Ypt32, or Myo2-Ypt32-SS—from the pRS413 plasmid can lose the YCp50-URA3-MYO2 plasmid and grow on the SD + 5-fluoroorotic acid (5-FOA) plate (top, right). Cells expressing the mutant proteins Myo2-Y1415R or the Myo2-Y1415R-Ypt32-SS cannot grow on SD + 5-FOA, whereas cells expressing the Myo2-Y1415R-Ypt32 fusion protein can lose the YCp50-URA3-MYO2 plasmid and grow on the SD + 5-FOA. Wild-type and mutant Myo2 proteins are expressed equally well (bottom, left). Strains were grown on SD-His-Ura, and lysates were analyzed for Myo2 expression by immunoblot analysis and antibodies against the Myo2-tail (top) or Pgk1p (loading control, bottom). Asterisk indicates Myo2p; arrow indicates the Myo2-Ypt32 fusion protein.