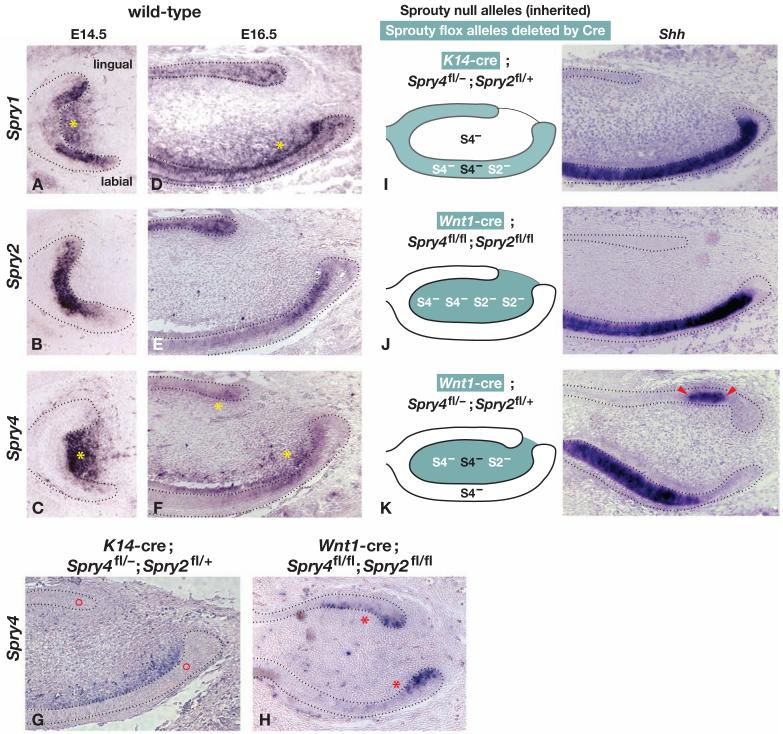
Figure 5. Sprouty gene expression and tissue-specific inactivation in the developing incisor.
Gene expression was analyzed by RNA in situ hybridization using the probes indicated on paraffin sections of embryonic incisors of the genotypes indicated at E16.5 or E17.5. (A-F) A comparison of the expression domains of Sprouty gene family members in the incisor at the stages indicated. Yellow asterisks indicate mesenchymal expression. (G-K) Tissue-specific inactivation of Spry4. The absence of Spry4 expression is indicated by red circles in the epithelium of an incisor carrying K14-cre, one Spry4fl and one Spry4- allele (panel G) and by red asterisks in the mesenchyme of an incisor carrying Wnt1-cre and two Spry4fl alleles (panel H). For each genotype shown in panels I-K, the diagram illustrates the tissue in which Cre-mediated recombination occurred (green fill), the Sprouty alleles that were inactivated by Cre (white lettering), or that were inherited as nulls (black lettering). The photograph shows Shh expression, which marks cells that are differentiating along the ameloblast lineage. The red arrowheads point to the ectopic lingual Shh expression domain.