Figure 1. MlotiK1 nucleotide selectivity of binding and activation.
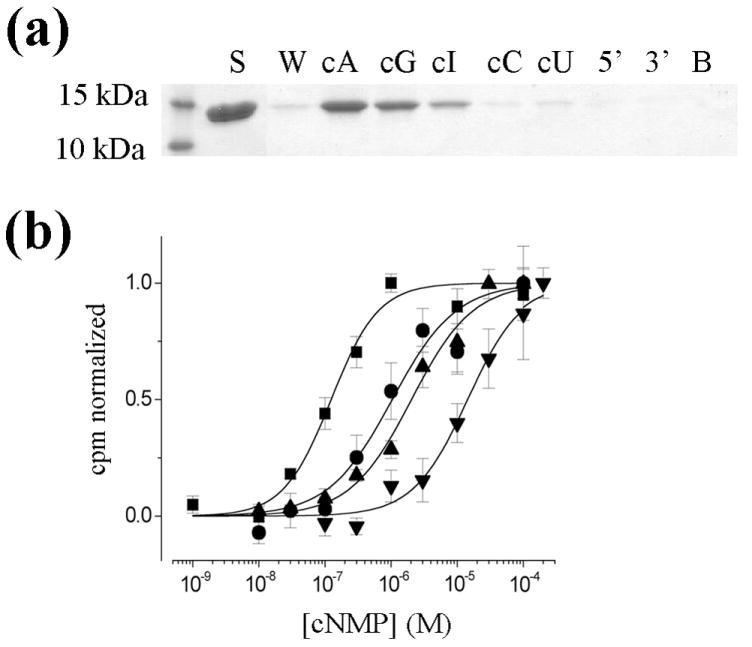
a). Immobilized agarose elution assay. Purified MlotiK1 CNB domain was bound to cAMP-immobilized agarose and 3 mM of the indicated nucleotide was added to the slurry to elute the protein from the agarose. Equal volumes of the elutions were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Coomassie staining. Nucleotides tested were adenosine 3’:5’ cyclic monophosphate (cA), guanosine 3’:5’ cyclic monophosphate (cG), inosine 3’:5’ cyclic monophospate (cI), cytidine 3’:5’ cyclic monophosphate (cC), uridine 3’:5’ cyclic monophosphate (cU), 5’ adenosine monophosphate (5’) and 3’ adenosine monophosphate (3’). S refers to the starting material while W is the wash and B is a buffer-only control. b) Concentration dependence of nucleotide-mediated uptake in wild-type MlotiK1. The various concentrations of cNMPs (1nM-300μM) were added to vesicles reconstituted with MlotiK1. Uptake at 90 min was normalized to basal uptake in the absence of nucleotide (0.0) and the maximal uptake measured for each nucleotide (1.0). Symbols and errors show mean ± SEM for 3-11 independent determinations. Solid lines show Hill fits to the data. Parameters from the fits – cAMP (■): K½ = 110 ± 16 nM and a Hill coefficient (n) of 1.3 ± 0.23; cGMP (●): K½ = 920 ± 109 nM, n = 1.1 ± 0.13; cIMP (▲): K½ = 2.1 ± 0.20 μM, n = 0.95 ± 0.10; cCMP (▼): K½ = 15 ± 3 μM, n = 1.05 ± 0.11.
