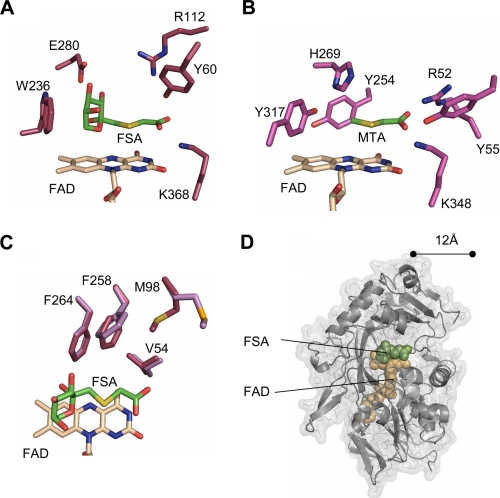
FIGURE 4.
Comparison of FAOX-II and MSOX actives sites. A, FSA bound to FAOX-II. B, methyl-thioacetate (MTA) bound to MSOX. His-269 in MSOX and Glu-280 in FAOX-II bind to the fructosamine hydroxyl groups. The Arg-52–Tyr-55—Lys-348 triad in MSOX and the Tyr-60–Arg-112–Lys-368 triad in FAOX-II interact with the inhibitor carboxylate. C, FAOX-II hydrophobic pocket. Met-98 and Phe-258 undergo slight rearrangement upon FSA binding (light magenta in free FAOX-II, dark magenta in the ligand-bound structure). D, FAOX-II active site accessibility. The molecular surface of the inhibitor-bound FAOX-II structure is shown with the two flexible active site loops computationally removed. The FAD cofactor and FSA inhibitor are shown as beige and green space-filling spheres, respectively. With the flexible loops removed, both FAD and FSA are partially accessible to solvent and about 12 Å from the opening of the active site.