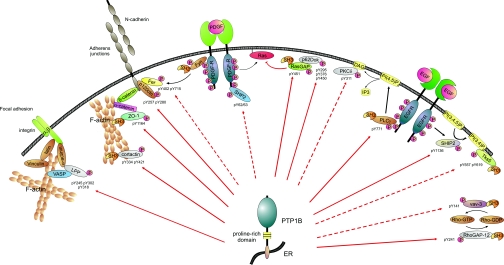
Fig. 6.
Schematic drawing summarizing novel potential PTP1B enzyme-substrate interactions in a functional context. ER-localized PTP1B contains a proline-rich domain that allows interaction with substrate proteins containing SH3 domains. Red arrows indicate a direct interaction and dephosphorylation of putative substrates, whereas dashed red arrows specify a direct or indirect functional association evident from increased tyrosine phosphorylation upon PTP1B deficiency. All depicted Tyr(P) sites are hyperphosphorylated in PTP1B-deficient cells. In addition, Tyr(P) sites of potential substrates were identified as putative interaction sites in the substrate-trapping assay. This scheme was designed on the basis of the following references: focal adhesion site (73), PDGFRβ-mediated regulation of N-cadherin cell-cell adhesion (47), and p62DOK and p120RasGAP regulation of Ras signaling (40). VASP, vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein; pY, phosphotyrosine; PI(4,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PI(3,4,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate; PI(3,4)P2, phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate.