Fig. 2.
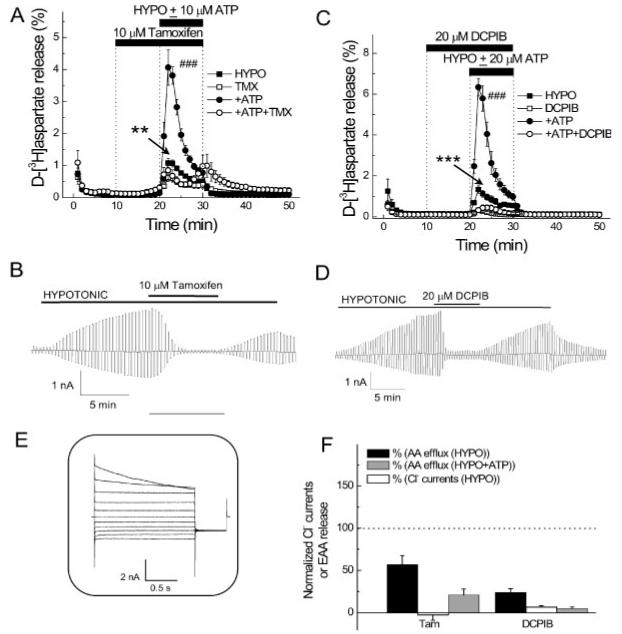
VRAC blockers DCPIB and tamoxifen potently inhibit swelling-activated D-[3H]aspartate release and Cl- currents in primary astrocyte cultures. A. Effect of 10 μM tamoxifen on swelling-activated D-[3H]aspartate release in the presence or absence of 10 μM ATP. Cells were exposed to hypo-osmotic medium (30% reduction in osmolarity for all experiments) as indicated, in the presence (□, ○) or absence (■, •) of 10 μM tamoxifen, applied as indicated. ATP was present in hypo-osmotic ∼ medium only (○, •). Data are means ±SEM of 5–7 experiments. **P = 0.002, tamoxifen vs. control; ###P < 0.001, ATP vs. ATP plus tamoxifen, repeated measures ANOVA. B. Effect of 10 μM tamoxifen on swelling-activated Cl- currents. Cells were held at 0 mV and step pulses to + and -40 mV were applied. Representative of six electrophysiological recordings. C. Effect of 20 μM DCPIB on swelling-activated D-[3H] aspartate release in the presence or absence of 20 μM ATP, in the presence (□, ○)or absence (■, •) of DCPIB, which was given 10 min before and during application of hypo-osmotic medium, as indicated. Data are means ± SEM of five experiments. ***P < 0.001, DCPIB vs. control; ***P < 0.001; ATP vs. ATP plus DCPIB, repeated measures ANOVA. D. Effect of 20-μM DCPIB on swelling-activated Cl- currents. Representative of six electrophysiological recordings. E. shows Cl- current responses to step pulses from -100 to +100 mV in 20-mV increments from 0-mV holding potential after exposure to hypotonic medium. F. Normalized release values relative to 100 for control swelling-activated excitatory amino acid release, with and without ATP and normalized VRAC currents in the absence of ATP in presence of tamoxifen or DCPIB. For B, D-F the isoosmotic external solution contained (in mM): 110 CsCl, 2 CaCl2, 1 MgSO4, 5 glucose, 10 Hepes, and 60 mannitol (pH 7.4, 290 mosmol). The hypoosmotic solution was made by omitting mannitol from isotonic solution and had an osmolarity of 230 mosmol. The pipette solution contained (in mM): 110 CsCl, 1 MgSO4, 1 Na2-ATP, 0.3 Na2-GTP, 15 Na-Hepes, 10 Hepes, and 1 EGTA (pH 7.3, 255 mosmol). The osmolarity of the pipette solution was set lower than that of the isotonic bath solution in order to prevent spontaneous cell swelling after attaining the whole-cell mode (from Abdullaev et al., 2006).
