Fig. 5.
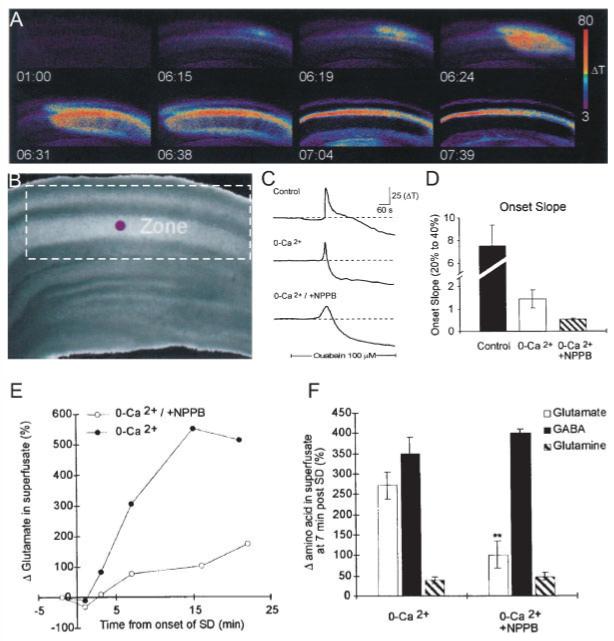
The release of glutamate during SD is reduced by NPPB, a blocker of volume-activated chloride channels. The release of glutamate during SD is reduced by NPPB, a blocker of volume-activated chloride channels, supporting a role for amino acid release due to astrocyte swelling. SD was triggered by inhibiting Na,K ATPase with ouabain. Imaging IOSs showed the progressive propagation of the depolarization and swelling during SD (A) (time in min; ΔT indicates increased light transmittance in arbitrary digital units) through the CA1 region (B) of the hippocampal brain slice. (C,D) SD still propagated in 0 external calcium, and NPPB in the absence of calcium reduced the onset slope of SD. The onset slope is the rate of change of transmittance during the propagation of SD. (E,F) NPPB also significantly reduced the efflux of glutamate during SD but did not alter GABA or glutamine efflux rates (from Basarsky et al., 1999). [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
