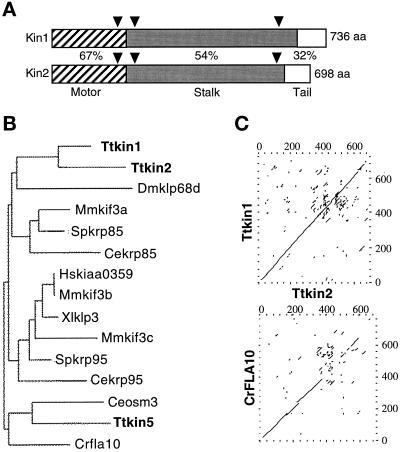
Figure 1.
KIN1 and KIN2 are kinesin-II homologous genes in Tetrahymena. (A) Diagram of the alignment of predicted KIN1 and KIN2 encoded protein sequences. Domains are indicated as follows: stripes, motor domain; gray, coiled coil stalk; white, globular tail. Percent identity between Kin1p and Kin2p in each domain is indicated. Triangles represent positions of introns in the corresponding genomic DNA. (B) Phylogram of kinesin-II proteins. Alignments of multiple sequences were prepared using PILEUP; evolutionary distances between sequences were calculated using DISTANCES; and an evolutionary tree was made using GROWTREE of the UWGCG system (Devereux et al., 1984). (C) Sequence comparison between KIN1 and KIN2 and between KIN2 and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii FLA10 (Walther et al., 1994). Dot matrix analysis was done using COMPARE and DOTPLOT programs of UWGCG. Sequence data used for comparisons are available from European Molecular Biology Laboratory, GenBank, and DNA Data Bank of Japan under accession numbers AJ244020 (KIN1), AJ244021 (KIN2), L33697 (Crfla10), D14968 (Ceosm3), AB002357 (Hskiaa0359), A57107 (Mmkif3b), C48835 (Xlklp3), AF013116 (Mmkif3c), U00996 (Spkrp95), U15974 (Dmklp68d), D12645 (Mmkif3a), and L16993 (Spkrp85). The sequence of Ttkin5 was provided by M. Bernstein (personal communication). The Cekrp85 and Cekrp95 sequences were identified by the C. elegans sequencing project (Signor et al., 1999).