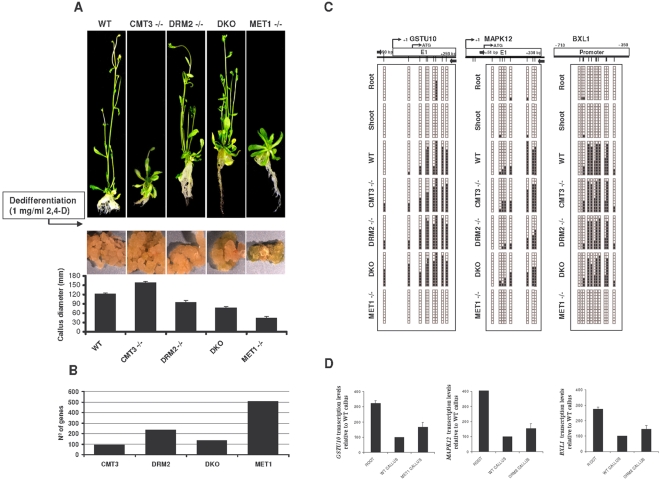
Figure 1. Promoter hypermethylation of Arabidopsis callus specifically depends on MET1 and DRM2 methyltransferase activity.
(A) Callus induction from DNA methyltransferases mutants. Upper panels, morphological aspect of entire plants grown from WT and DNA methyltransferase mutant seeds. Lower panels, growth rates of WT and mutant callus generated after treatment with 2,4-D of root explants. (B) Number of candidate genes susceptible to DNA methylation-dependent regulation obtained from each DNA methyltransferase mutant using the two-step criteria described in the Results section. (C) Bisulfite sequencing of twelve individual clones of the GSTU10, MAPK12 and BXL1 promoters in WT and DNA methyltransferase mutants. (D) Relationship between levels of GSTU10, MAPK12 and BXL1 expression and promoter DNA hypermethylation. Transcript levels of both genes were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR and results are expressed as a relative enrichment of the hypomethylated samples (roots and methyltransferase mutants) versus the hypermethylated samples (WT callus).