Fig. 4.
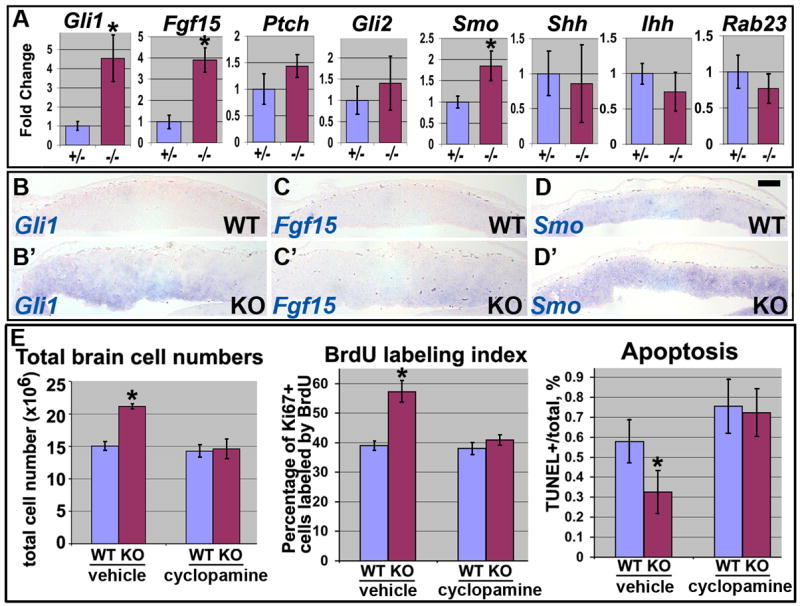
Activation of Hh pathway is responsible for shortening of cell cycle, decreased apoptosis and subsequent hyperplasia in αE-catenin−/− cerebral cortexes. (A) qPCR analysis of Hh pathway transcripts in E12.5 heterozygous and mutant brains. The levels of expression are shown in arbitrary units with mean heterozygous levels adjusted to one. Data represent means ± SD. N≥4. *P<0.002. (B–D′) Cortical sections from E12.5 wildtype and αE-catenin−/−embryos were analyzed by in situ hybridization with Gli1, Fgf15 and Smo probes. Bar in frame D represents 200km. (E) Inhibition of Hh pathway by cyclopamine eliminates thedifferences in total cell numbers, cell cycle length and apoptosis between the wildtype and αE-catenin−/− brains. Pregnant females were injected with 10mg/kg of cyclopamine in 2-hydropropyl-β-cyclodextrin (vehicle) or vehicle alone at E12.5 and embryos were analyzed 30h later. Quantitation was performed as described in Figs. 3, S2. Data represent means ± SD. N≥3. *P<0.001.
