Figure 5.
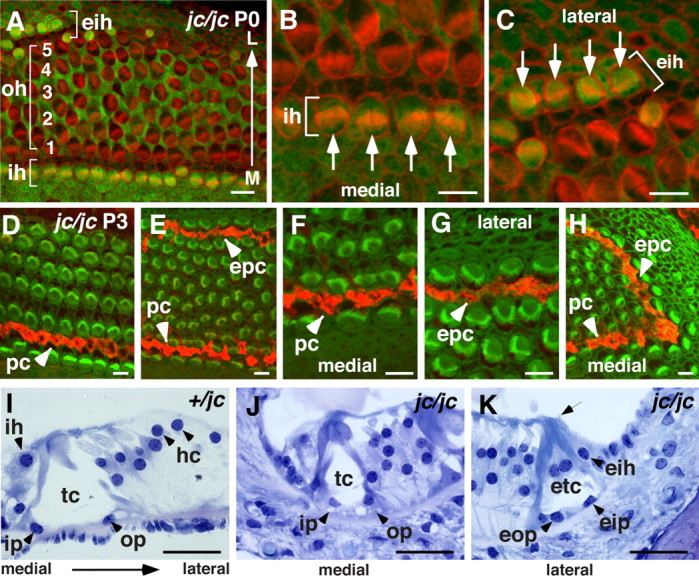
Ectopic tunnel of Corti and inner hair cells. A–H, Confocal images of organ of Corti whole-mount preparations. Apical region at age P0 stained for S100A1 (green) and phalloidin (red; A) shows a disorganized pattern of OHC rows (oh, bracket) followed by a stretch if IHCs located ectopically (eih, bracket) at the lateral (L) side of the organ of Corti. Location of IHCs at the medial (M) side is depicted (ih, bracket). B, Higher magnification of the medial location of four IHCs (ih, bracket, and arrows). C, The ectopically located IHCs at the lateral side of the organ of Corti (eih, bracket, and arrows). D–H, Immunostaining of the midapical (D) and apical region (E–H) of jc/jc at P3 for p75NTR (red; phalloidin, green). D–F, Location of pillar cells at the medial side is indicated (pc, arrowhead). E, A row of ectopic pillar cells at the lateral side of the organ of Corti is stained (epc, arrowhead). F, G, Higher-magnification images of pc and epc as shown in E. I–K, Plastic sections stained by toluidine blue O. I, Normal position of IHCs (ih), inner (ip) and outer (op) pillar cells, tunnel of Corti (tc), and Hensen's cells (hc) in a jc heterozygote. J, K, In jc mutants, an immature tunnel of Corti is shown at the medial side (J), and ectopic tunnel of Corti (etc) formed by ectopic outer (eop) and inner (eip) pillar cells followed by an IHC is shown at the lateral side (K). Note the stereociliary hair bundle of the ectopic IHC (arrow). Scale bars: A–H, 10 μm; I–K, 50 μm.
