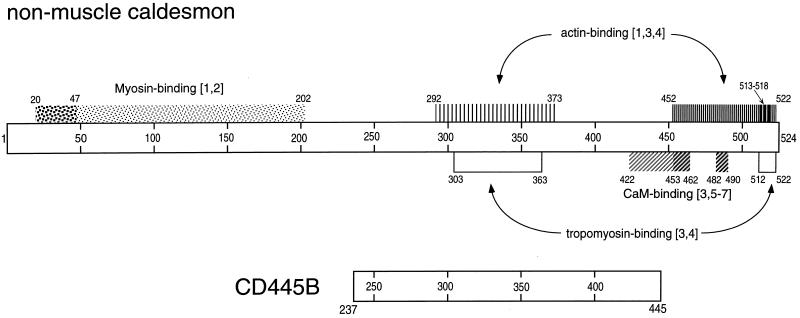
Figure 1.
Functional domains of nonmuscle caldesmon and a truncated caldesmon variant. Putative functional domains of the nonmuscle caldesmon molecule were determined by alignment of the nonmuscle and smooth muscle caldesmon using Clustal View software (Higgins et al., 1991). Tropomyosin-binding domains are shown as open bars; myosin-binding domains are shown as spotty bars (the larger square spots correspond to stronger binding); actin- and calmodulin-binding domains are indicated by vertically and obliquely hatched bars, respectively (the density of hatching corresponds to the strength of binding). The digits at the ends of the bars and inside the bars correspond to the numbers of amino acid residues on caldesmon. The numbers in brackets indicate the following references: [1], Yamashiro et al. (1995); [2], Wang et al. (1997); [3], Wang et al. (1996); [4], Wang and Chacko (1996); [5], Marston et al. (1994); [6], Mezgueldi et al. (1994); and [7], Zhuang et al. (1995).