Figure 1.
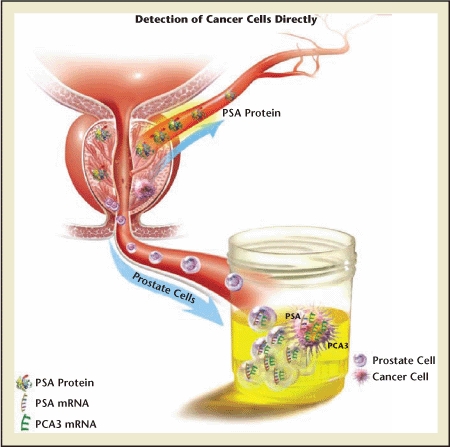
Diagram showing urinary prostate cancer antigen 3 (PCA3) (lower arrow) versus serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) (upper arrow). Whereas PSA is a glycoprotein that may enter the bloodstream, PCA3 is a gene that exists in the nuclear material of prostate epithelial cells and that may be shed into the urine. Those cells, if cancerous, overexpress the gene. That overexpression, which may be many times that found in benign prostate cells, is detected by the assay. Importantly, PCA3 expression is normalized against a background of prostate-specific nuclear material (PSA messenger ribonucleic acid [mRNA]), yielding a PCA3 score. The PCA3 score is much more cancer-specific than serum PSA levels, which are confounded by factors such as prostate volume, age, trauma, and certain drugs.
