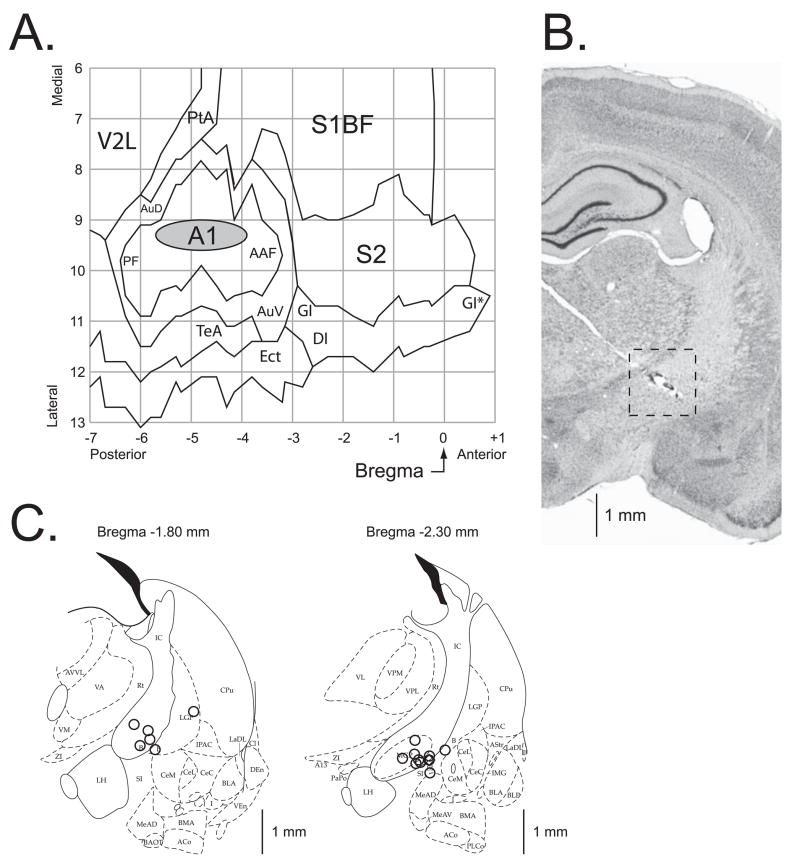
Figure 6.
Location of recording and stimulation sites. (A) The auditory cortex EEG recording location. The oval indicates the location of epidural recordings based on their stereotaxic coordinates using a cortical map derived from Paxinos and Watson (1997). The location of the sites for each individual subject in the Saline and Scopolamine groups were precisely measured; they all were found to be over the primary auditory cortex. The sites of recording in Saline and Scopolamine groups overlapped, did not differ statistically (see Results) and thus are shown as a single group. (B) A section stained for Nissl showing the electrode track and the place of lesion (the site of stimulation) in the nucleus basalis. The electrode was implanted by a contralateral approach, to avoid damage to ipsilateral structures. (C) Diagrams of the two coronal sections (AP = −1.8 mm and AP = −2.3 mm) showing the NB stimulation sites; the sites were projected onto outlines of frontal section at closest relevant sections Anterior-to-Posterior (AP) distance relative to Bregma in millimeters (Paxinos & Watson, 1997). The stimulation sites in the Saline and the Scopolamine groups were intermingled and did not differ statistically (see Results) and thus are shown as a single group. In all animals, stimulation was within the caudal nucleus basalis (ventrolateral internal capsule, ventromedial lateral globus pallidus and nucleus basalis of Meynart) which projects preferentially to the auditory cortex. Small open circles represent individual stimulation sites. The scale bars in (B) and (C) are roughly equal thus providing a better view on where within the right intracranial region the stimulation sites were located. Abbreviations: B, basal nucleus of Meynert; CeM, amygdala central nucleus medial; CeL, amygdala central nucleus lateral; CPu, caudate–putamen; IC, internal capsule; IPAC, interstitial nucleus of posterior limb of anterior commissure; LGP, lateral globus pallidus; LH, lateral hypothalamus; SI, substantia innominata; SIB, substantia innominata, basal; SIV, substantia innominata, ventral; Au, primary auditory cortex; AAF, anterior auditory Weld; AuD, secondary auditory cortex, dorsal; AuV, secondary auditory cortex, ventral; PF, posterior auditory Weld; S1BF, primary somatosensory cortex, barrel Weld; S2, secondary somatosensory cortex; TeA, temporal association cortex; V2L, secondary visual cortex, lateral area.