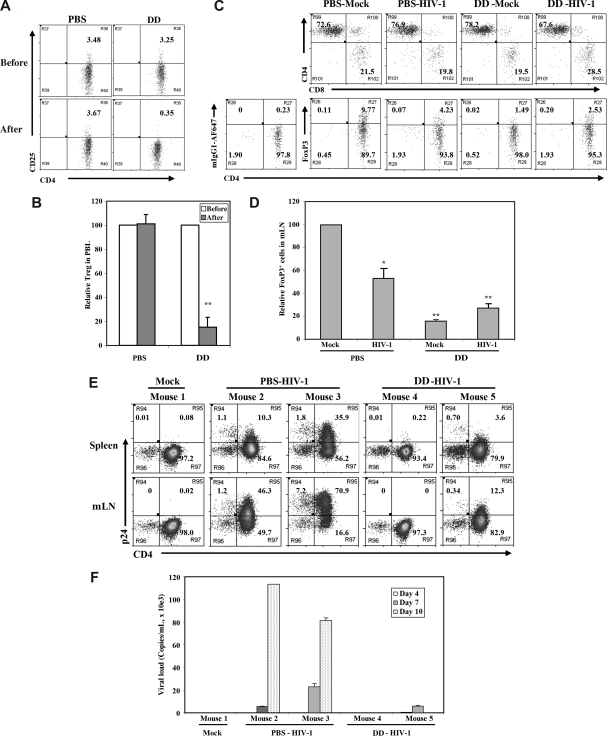
Figure 6.
Denileukin diftitox (DAB389IL-2) treatment depleted Treg cells and reduced HIV-1 infection in DKO-hu HSC mice. (A) Human CD4+CD25+/hi Treg cells in peripheral blood of DKO-hu HSC mice were analyzed by FACS 24 hours after PBS or denileukin diftitox injection. Shown are CD45+CD3+CD4+ T cells. (B) Relative depletion of CD4+CD25+ T cells in the blood was shown, using preinjection levels as 100. Error bars are standard deviations (n = 4 DKO-hu mice for PBS or denileukin diftitox). (C) Forty-eight hours after PBS or denileukin diftitox injection, DKO-hu HSC mice were infected with HIV-R3A virus. At 7 days after infection, mLN from HIV-1– and mock-infected mice were analyzed for CD4/CD8 or CD4/FoxP3 expression by FACS. Shown are pregated CD45+CD3+ human T cells for CD4/CD8 and CD45+CD3+CD8− human T cells for CD4/FoxP3. Numbers indicate percentage of each cell population, and mIgG1-AF647 was used as isotype control for the FoxP3 staining. (D) Relative percentage of FoxP3+CD3+CD8− Treg cells is summarized with data from 2 to 4 mice. (E) DKO-hu mice were similarly treated as in panel C and infected with mock or HIV-R3A. At 10 days after infection, CD45+CD3+CD8− T cells from spleen or mLN were analyzed for expression of CD4 and p24 by FACS. (F) HIV-1 viremia in plasma samples (copies/mL) from all infected DKO-hu mice were measured at 4, 7, and 10 days after infection. Data shown are representative of 3 independent experiments with 2 to 3 mice in each group. Error bars indicate standard deviations.