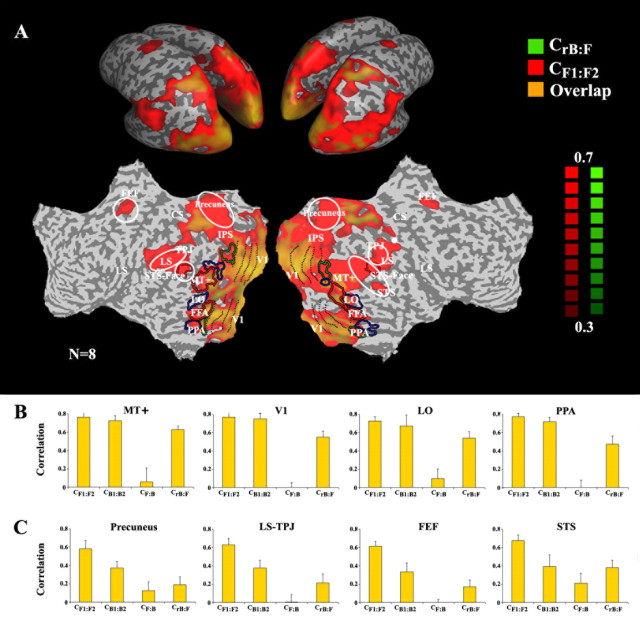
Figure 2.
Effect of time reversal across the cortical surface. A, Maps of the correlations between the two forward time courses (CF1:F2, red) and the reversed-backward and forward time courses (CrB:F, green). Regions in which the responses were time-reversible exhibit both high CF1:F2 and high CrB:F (overlap, orange). Correlation maps are shown on inflated (top) and unfolded (bottom) left and right hemispheres. The maps show only voxels for which the correlation exceeded a threshold value (0.3, chosen because it was above the highest CF,B value exhibited by any voxel). CrB:F was high in a number of posterior cortical regions, indicating that the responses to the backward films were a simple time reversal of the responses to the forward films. In other brain regions, we observed high CF1:F2, but low CrB:F (red). White outlines mark the main regions in which responses were not time reversible. Anatomical abbreviations: ITS, inferior temporal sulcus; LS, lateral sulcus; STS, superior temporal sulcus; TPJ, temporal parietal junction; CS, central sulcus; IPS, intraparietal sulcus. Several higher-order visual areas were functionally defined based on their responses to faces (red outlines), objects (blue outlines), and houses (green outlines). Functionally and anatomically defined cortical areas: V1, primary visual cortex; MT+, MT complex responsive to visual motion; PPA, parahippocampal place area; FFA, fusiform face area; LO, lateral occipital complex responsive to pictures of objects; STS-face, area in superior temporal sulcus responsive to faces. B, Reliability of response time courses for regions that exhibited time-reversible responses: MT+, V1, LO, and PPA. In each of these cortical regions, the values of CrB:F and CB1:B2 were similar to the CF1:F2 values. Error bars represent the SEM across nonoverlapping movie segments. C, Brain regions in which responses were not time reversible (white outlines in A): precuneus, posterior LS, TPJ, FEFs, and the posterior STS. In each of these cortical regions, the values of CB1:B2 and CrB:F were much less than CF1:F2.