Abstract
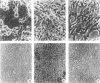
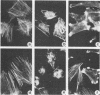
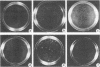
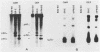
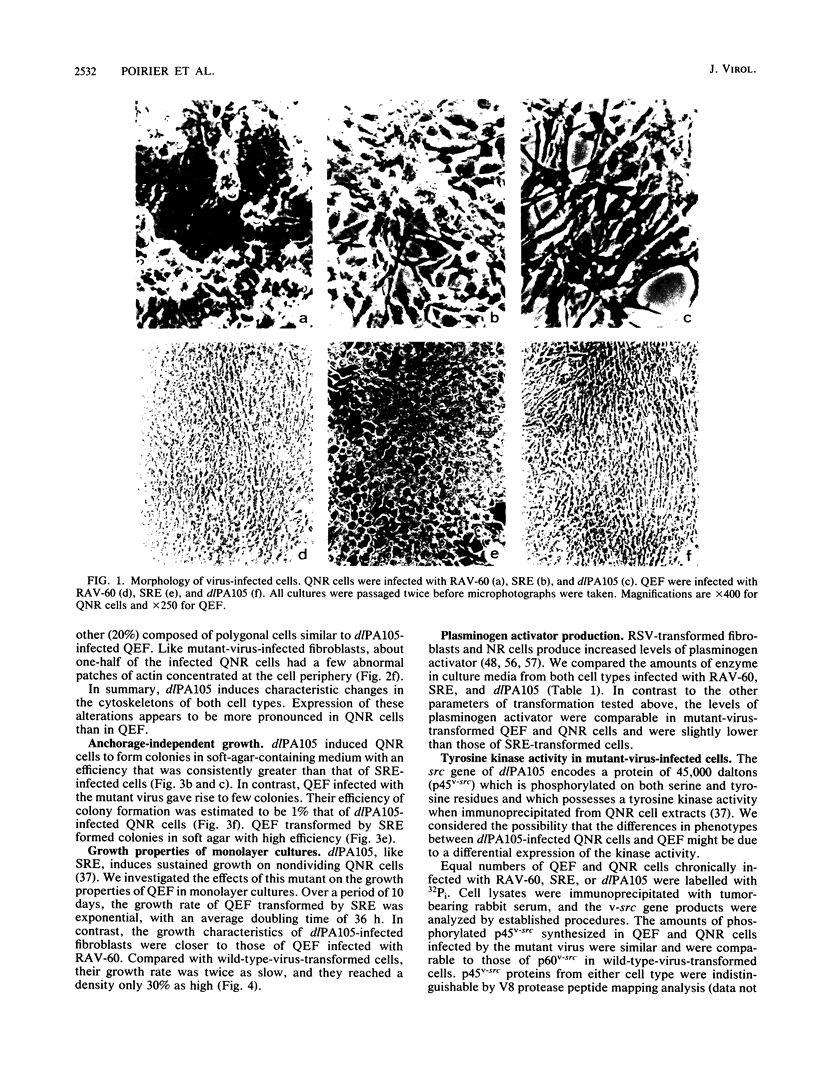
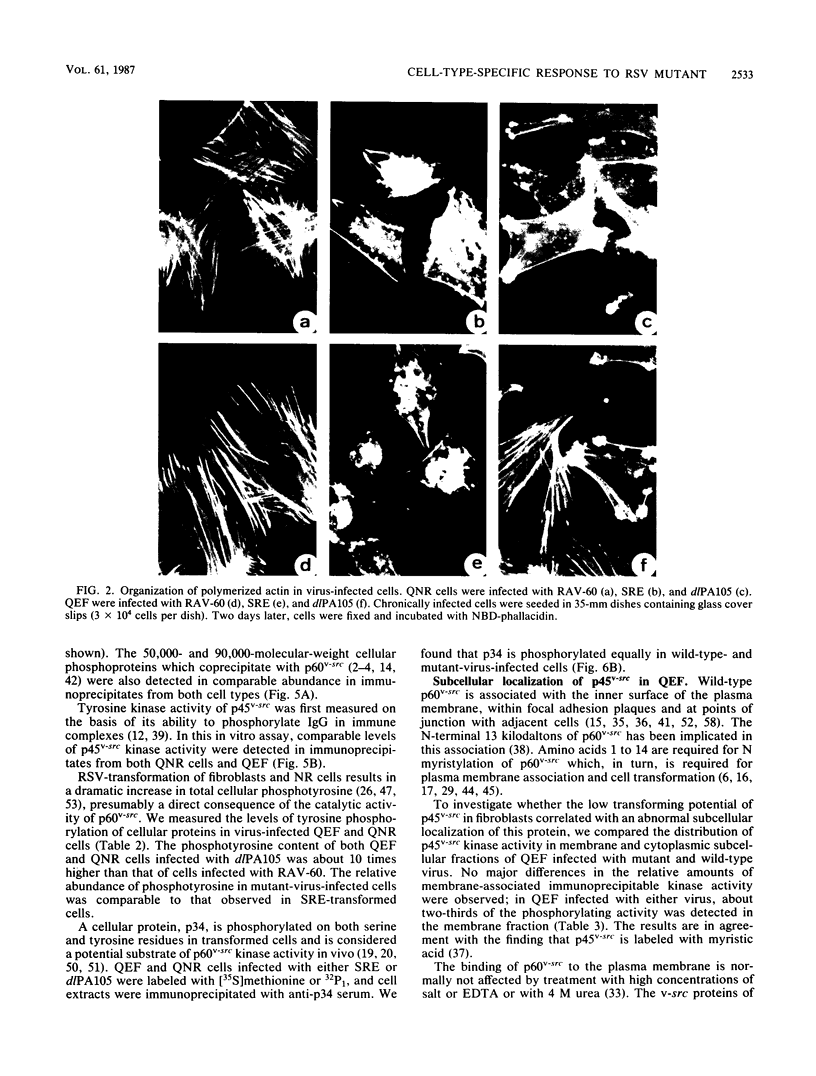
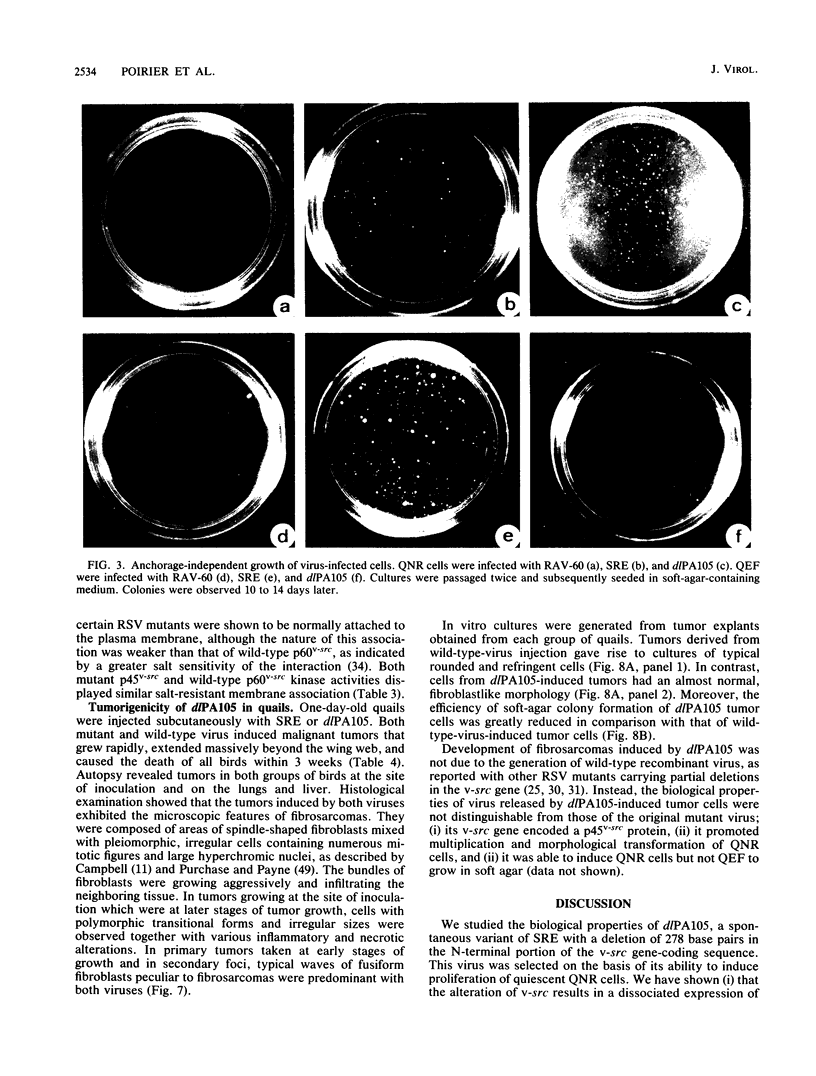
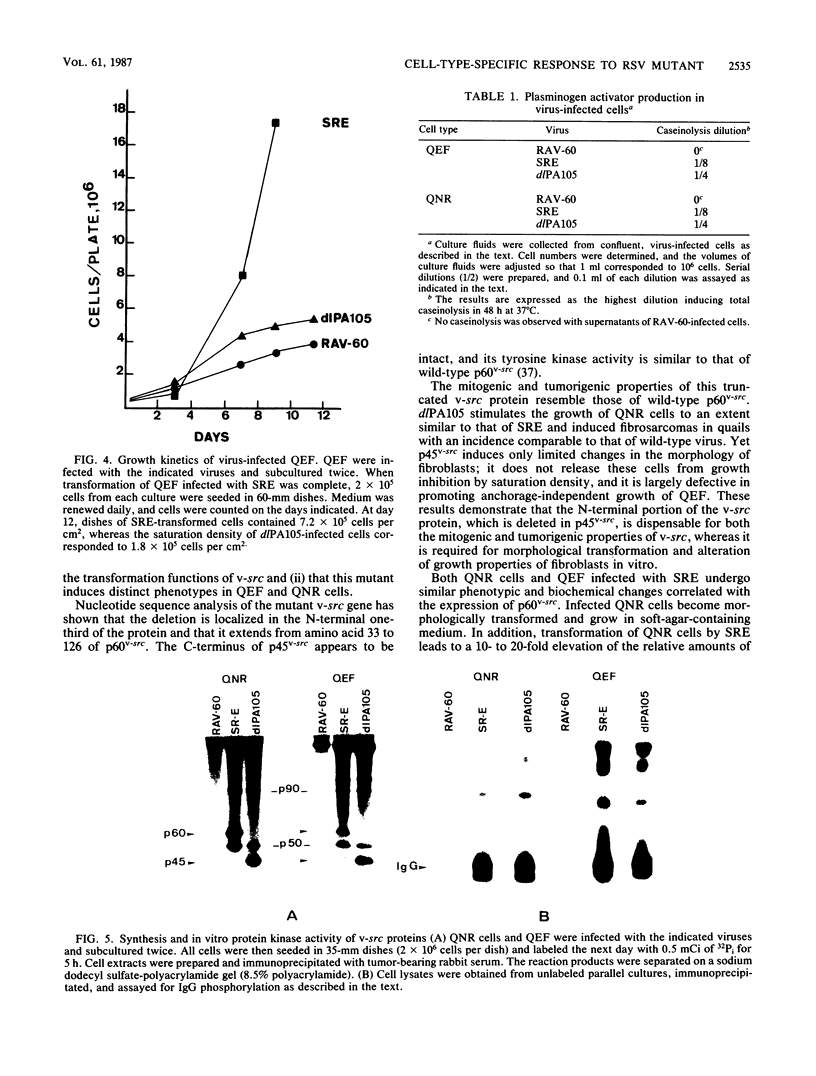
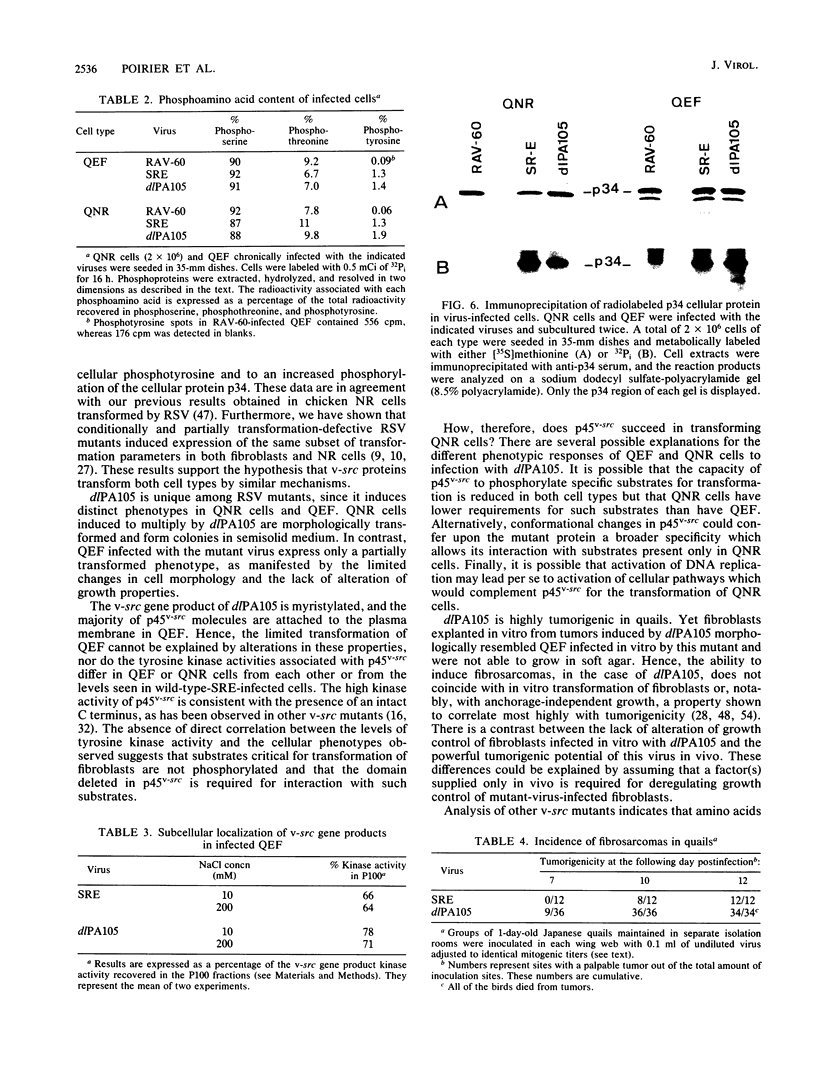
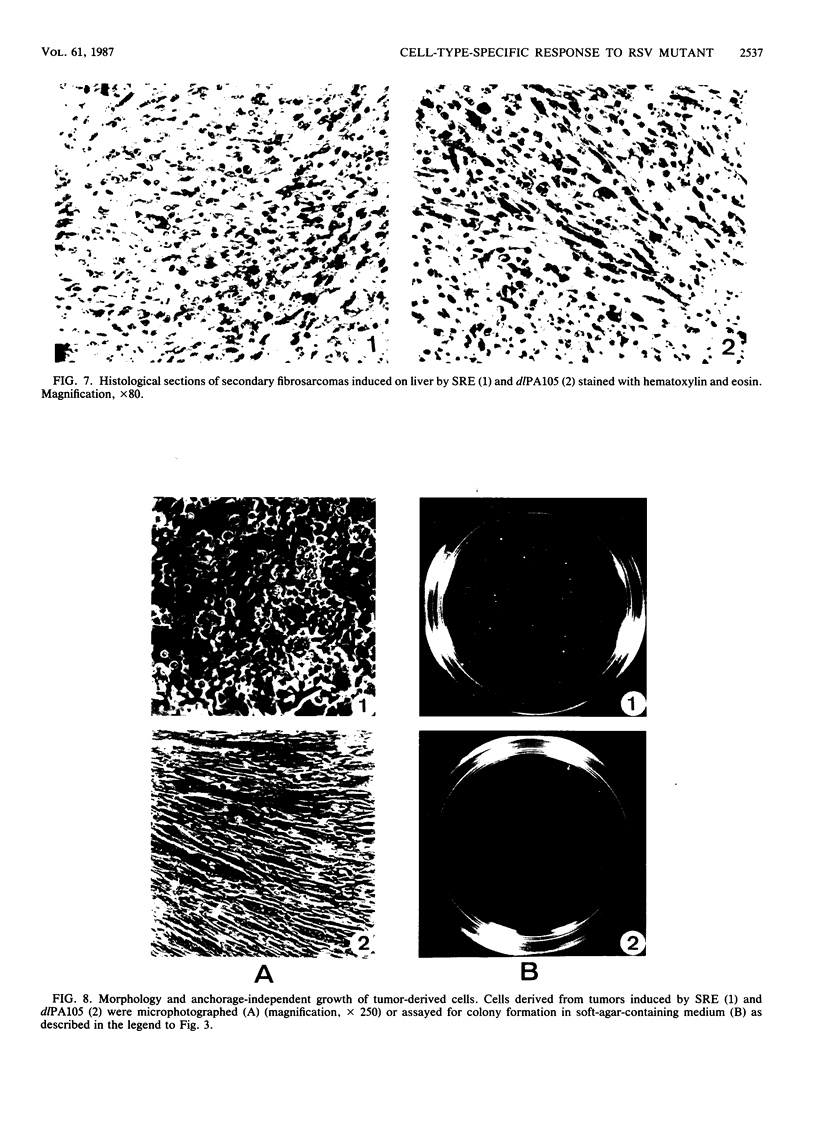
dlPA105 is a spontaneous variant of Rous sarcoma virus, subgroup E, which carries a deletion in the N-terminal portion of the v-src gene coding sequence. This virus was isolated on the basis of its ability to induce proliferation of quiescent quail neuroretina cells. The altered v-src gene encodes a phosphoprotein of 45,000 daltons which possesses tyrosine kinase activity. DNA sequencing of the mutant v-src gene has shown that deletion extends from amino acid 33 to 126 of wild-type p60v-src. We investigated the tumorigenic and transforming properties of this mutant virus. dlPA105 induced fibrosarcomas in quails with an incidence identical to that induced by wild-type virus. Quail neuroretina cells infected with the mutant virus were morphologically transformed and formed colonies in soft agar. In contrast, dlPA105 induced only limited morphological alterations in quail fibroblasts and was defective in promoting anchorage-independent growth of these cells. Synthesis and tyrosine kinase activity of the mutant p45v-src were similar in both cell types. These data indicate that the portion of the v-src protein deleted in p45v-src is dispensable for the mitogenic and tumorigenic properties of wild-type p60v-src, whereas it is required for in vitro transformation of fibroblasts. The ability of dlPA105 to induce different transformation phenotypes in quail fibroblasts and quail neuroretina cells is a property unique to this Rous sarcoma virus mutant and provides evidence for the existence of cell-type-specific response to v-src proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barak L. S., Yocum R. R., Nothnagel E. A., Webb W. W. Fluorescence staining of the actin cytoskeleton in living cells with 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole-phallacidin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):980–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Darrow D. Rous sarcoma virus-induced phosphorylation of a 50,000-molecular weight cellular protein. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):250–253. doi: 10.1038/295250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. The specific interaction of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, pp60src, with two cellular proteins. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J., Yonemoto W., Darrow D. Interaction between the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein and two cellular phosphoproteins: analysis of the turnover and distribution of this complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):9–19. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Kamps M. P., Gould K., Sefton B. M. The absence of myristic acid decreases membrane binding of p60src but does not affect tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):468–474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.468-474.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calothy G., Laugier D., Cross F. R., Jove R., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. The membrane-binding domain and myristylation of p60v-src are not essential for stimulation of cell proliferation. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1678–1681. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1678-1681.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calothy G., Pessac B. Growth stimulation of chicl embryo neuroretinal cells infected with Rous sarcoma virus: relationship to viral replication and morphological transformation. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):336–345. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calothy G., Poirier F., Dambrine G., Mignatti P., Combes P., Pessac B. Expression of viral oncogenes in differentiating chick embryo neuroretinal cells infected with avian tumor viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):983–990. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calothy G., Poirier F., Dambrine G., Pessac B. A transformation defective mutant of Rous sarcoma virus inducing chick embryo neuroretinal cell proliferation. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L. Avian sarcoma virus-transforming protein, pp60src shows protein kinase activity specific for tyrosine. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):167–169. doi: 10.1038/285167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Transit of pp60v-src to the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7117–7121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Levinson A. D., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus (pp60src) and a homologous protein in normal cells (pp60proto-src) are associated with the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3783–3787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. N-terminal deletions in Rous sarcoma virus p60src: effects on tyrosine kinase and biological activities and on recombination in tissue culture with the cellular src gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2789–2795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David-Pfeuty T., Singer S. J. Altered distributions of the cytoskeletal proteins vinculin and alpha-actinin in cultured fibroblasts transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6687–6691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Cook R., Miller G. J., Erikson R. L. The same normal cell protein is phosphorylated after transformation by avian sarcoma viruses with unrelated transforming genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;1(1):43–50. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of a cellular protein substrate phosphorylated by the avian sarcoma virus-transforming gene product. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita D. J., Bechberger J., Nedic I. Four Rous sarcoma virus mutants which affect transformed cell morphology exhibit altered src gene products. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):256–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Processing of p60v-src to its myristylated membrane-bound form. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2781–2788. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. R. Increased protease levels in transformed cells: a casein overlay assay for the detection of plasminogen activator production. Cell. 1974 Jun;2(2):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H., Halpern C. C., Buchhagen D. L., Kawai S. Recovery of avian sarcoma virus from tumors induced by transformation-defective mutants. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1735–1747. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Mayer B. J., Iba H., Laugier D., Poirier F., Calothy G., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Genetic analysis of p60v-src domains involved in the induction of different cell transformation parameters. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):840–848. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.840-848.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn P., Nakamura K., Shin S., Smith R. E., Weber M. J. Tumorigenicity of partial transformation mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):602–611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.602-611.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Hanafusa H. Viral and cellular src genes contribute to the structure of recovered avian sarcoma virus transforming protein. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90511-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Hayward W. S., Hanafusa H. Cellular information in the genome of recovered avian sarcoma virus directs the synthesis of transforming protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3154–3158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Yoshida M. Small deletion in src of Rous sarcoma virus modifying transformation phenotypes: identification of 207-nucleotide deletion and its smaller product with protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):985–992. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.985-992.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Garber E. A., Goldberg A. R., Hanafusa H. Changes in amino-terminal sequences of pp60src lead to decreased membrane association and decreased in vivo tumorigenicity. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):889–896. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Garber E. A., Goldberg A. R. Subcellular localization of pp60src in RSV-transformed cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;107:51–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Wang E., Goldberg A. R. Evidence that the src gene product of Rous sarcoma virus is membrane associated. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):25–40. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90480-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzyzek R. A., Mitchell R. L., Lau A. F., Faras A. J. Association of pp60src and src protein kinase activity with the plasma membrane of nonpermissive and permissive avian sarcoma virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):805–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.805-815.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laugier D., Marx M., Barnier J. V., Poirier F., Genvrin P., Dezélée P., Calothy G. N-terminal deletion in the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus results in synthesis of a 45,000-Mr protein with mitogenic activity. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2523–2529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2523-2529.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Structural and functional domains of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein (pp60src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Evidence that the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus encodes a protein kinase associated with a phosphoprotein. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The purified product of the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11973–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Walter G., Singer S. J. Immunofluorescent localization of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus with antibodies against a synthetic src peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5322–5326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Kawai S. Two cellular proteins that immunoprecipitate with the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):736–751. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. An N-terminal peptide from p60src can direct myristylation and plasma membrane localization when fused to heterologous proteins. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):374–377. doi: 10.1038/314374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Fine structural mapping of a critical NH2-terminal region of p60src. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1623–1627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessac B., Calothy G. Transformation of chick embryo neuroretinal cells by Rous sarcoma virus in vitro: induction of cell proliferation. Science. 1974 Aug;185(4152):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4152.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier F., Calothy G., Karess R. E., Erikson E., Hanafusa H. Role of p60src kinase activity in the induction of neuroretinal cell proliferation by rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):780–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.780-789.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier F., Jullien P., Dezelee P., Dambrine G., Esnault E., Benatre A., Calothy G. Role of the mitogenic property and kinase activity of p60src in tumor formation by Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):325–332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.325-332.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: a cellular substrate for transformation-specific protein phosphorylation contains phosphotyrosine. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: effects of src gene expression on the synthesis and phosphorylation of cellular polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5212–5216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R. Adhesion plaques of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells contain the src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3514–3518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K., Eckhart W. Evidence that the phosphorylation of tyrosine is essential for cellular transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90327-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin S. I., Freedman V. H., Risser R., Pollack R. Tumorigenicity of virus-transformed cells in nude mice is correlated specifically with anchorage independent growth in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4435–4439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Enrietto P. J., Wyke J. A. Functional domains of the pp60v-src protein as revealed by analysis of temperature-sensitive Rous sarcoma virus mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1508–1514. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Tobia A., Ossowski L., Quigley J. P., Rifkin D. B., Reich E. An enzymatic function associated with transformation of fibroblasts by oncogenic viruses. I. Chick embryo fibroblast cultures transformed by avian RNA tumor viruses. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):85–111. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J., Dano K., Kellerman G. M., Reich E. Fibrinolysis associated with oncogenic transformation. Partial purification and characterization of the cell factor, a plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4295–4305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Jay G., Pastan I. Localization of the ASV src gene product to the plasma membrane of transformed cells by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90361-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]