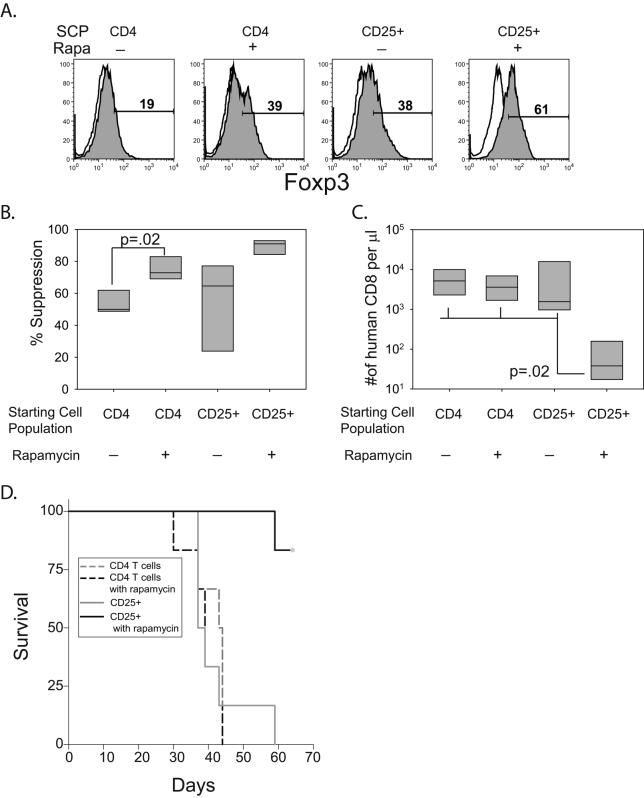
Figure 5. In vivo prevention of xeno GVHD of T regs expanded with CD28 and rapamycin.
A. A Starting cell population (SCP) of 2×105 CD4 bulk T cells (CD4) or enriched Tregs (CD25+) were stimulated with K64.86 aAPCs in the presence or absence of rapamycin. After two weeks of culture, Foxp3 (filled) expression and isotype control Ab (open) staining was measured by flow cytometry. B. In vitro suppression of each population described in A was measured as described in Fig4. Data represents four independent experiments. C. 2 million cells from each culture shown in A. were mixed with 10 million autologous PBMCs and injected into NOG mice (6 mice per group). After 8 weeks, the mice were bled and the number of human CD8+ T cells/μl of blood was determined. D. Kaplan-Meier Survival Analysis (Log-Rank) was performed with the indicated cohorts of mice. The Holm-Sidak method for multiple comparisons (significance level = 0.05) was performed in all groups and significant differences were found between in the mice that were treated with enriched Tregs expanded in the presence of rapamycin and all other groups.