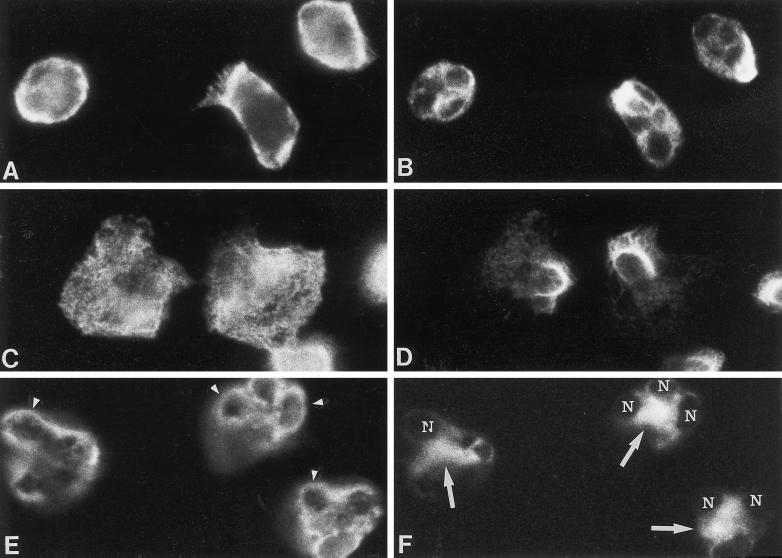
Figure 2.
Effect of cytochalasin D on intermediate filament and microfilament organization in neutrophils stimulated with fMLP for 2.5 min. Dual-label immunofluorescence localization of actin (left panel) and vimentin (right panel) is shown in unstimulated neutrophils (A and B) and cells stimulated with fMLP in the absence (C and D) and presence of cytochalasin D (E and F). Vimentin filaments are removed from areas containing microfilaments after fMLP stimulation (C and D). The localization of actin and vimentin in neutrophils treated with cytochalasin D alone (our unpublished results) was similar to that of control neutrophils (A and B). However, fMLP with cytochalasin D (E and F) induced the accumulation of actin around the nuclear lobes (arrowheads) and vimentin at the cell center (arrows) within the nuclear clef (nucleus, N). Another plane of focus demonstrated that vimentin was organized as filaments within the nuclear clef and that aggregates of actin were distributed at the cell cortex. Magnification, 1800×.