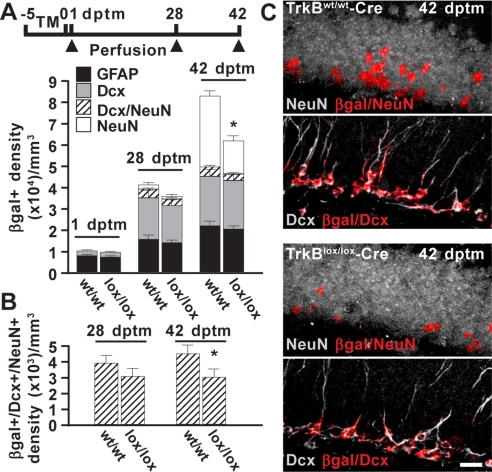
Fig. 1.
Deletion of TrkB affects the survival of newborn neurons. (A) Schematic diagram showing the experimental paradigm used for tamoxifen-induced Cre recombination in TrkBlox/lox-Cre R26R mice and control littermates. Histograms depict the density distribution of reporter-positive cells (βgal+) expressing GFAP, Dcx, or NeuN in TrkBwt/wt-Cre (wt/wt) and TrkBlox/lox-Cre (lox/lox) mice. (B) Density of reporter-positive cells coexpressing Dcx and NeuN as in A. Ten slices per hemisphere and two mice for each time point were analyzed (*, P < 0.05). (C) Representative confocal images depict the reporter marker βgal colocalized with either the neuronal marker NeuN (βgal/NeuN) or Dcx (βgal/Dcx). Colocalization signals (red) were superimposed on NeuN or Dcx immunoreactivity (gray). Labeling of each single marker from which colocalization was obtained is shown as SI Materials and Methods (see Fig. S2). (Scale bar, 20 μm.)