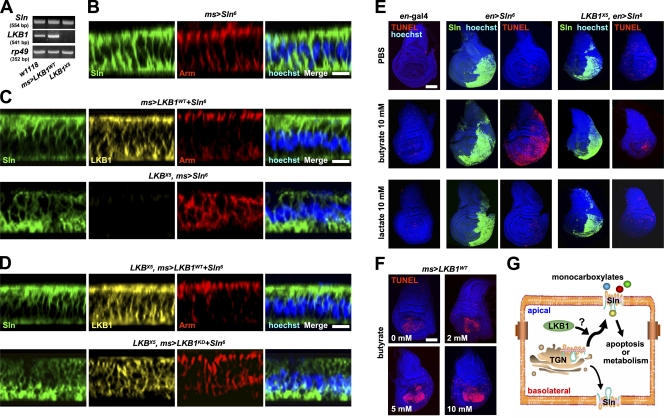
Figure 5.
LKB1 induces apical trafficking of Sln to mediate butyrate-induced apoptosis. (A) RT-PCR analyses of Sln and LKB1 transcripts in larval wing discs from the indicated genotypes. rp49 was used as a loading control. (B–D) Confocal z-stack analyses of the immunostaining against Myc (Sln; green), LKB1 (yellow), armadillo (Arm; red), and hoechst (DNA; blue) in larval wing discs from the indicated genotypes. The penetrances of Sln polarity phenotypes were 100, 100, 73, 100, and 67% (from top to bottom), respectively (n = 15). Bars, 5 μm. (E and F) TUNEL (red) and hoechst (DNA; blue) staining and Myc (Sln; green) immunostaining in larval wing discs from the indicated genotypes after stimulation with the indicated concentrations of butyrate or lactate. Bars, 50 μm. (G) A proposed model of the interplay between LKB1 and Sln in polarized cells. LKB1 induces apical trafficking of Sln, promoting the transport of extracellular monocarboxylates that may act as metabolites or apoptosis inducers. TGN, trans-Golgi networks.