Figure 1.
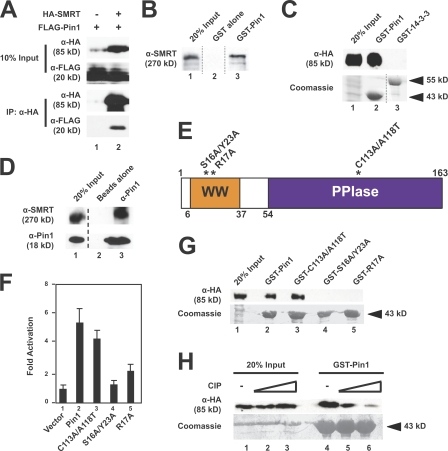
Pin1 is a SMRT-associating protein. (A) Transfected SMRT and Pin1 interact in mammalian cells. HeLa cells were transfected with either FLAG-Pin1 alone or with both FLAG-Pin1 and HA-SMRT (1,178–1,823). WCEs expressing these proteins were subjected to coimmunoprecipitation with α-HA–conjugated agarose beads followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) Pin1 interacts with SMRT in vitro. Purified, immobilized GST–Pin1 fusion protein was incubated with HeLa nuclear extracts, and bead fractions were subjected to immunoblotting with α-SMRT antibodies. (C) SMRT interacts with Pin1 but not 14-3-3ε. GST pull downs were performed using purified GST–Pin1, GST–14-3-3ε, and HeLa WCEs expressing HA-SMRT (1,178–1,823). Top, immunoblotting with α-HA; bottom, Coomassie staining. (D) Endogenous SMRT and Pin1 interact in mammalian cells. HeLa nuclear extracts were subjected to coimmunoprecipitation with Pin1 antibodies and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Unrelated lanes were removed. (E) Schematic representation of human Pin1. Point mutations used in this study are indicated by *. Pin1 contains both a WW domain and a PPIase domain. Amino acids are indicated by numbers. (F) The Pin1 WW domain is critical for interaction with SMRT in yeast. Y190 cells expressing GAL4 DBD SMRT (1,178–1,823) and the indicated GAL4 activation domain Pin1 constructs were subjected to β-galactosidase assays as described in Materials and methods. Error bars represent ±SD. (G) The Pin1 WW domain is essential for SMRT association in vitro. GST pull downs were performed using the indicated GST–Pin1 proteins and HeLa WCEs expressing HA-SMRT (1,178–1,823). Top, immunoblotting with α-HA; bottom, Coomassie staining. (H) Phosphatase treatment disrupts the SMRT–Pin1 interaction in vitro. HeLa WCEs expressing HA-SMRT (1,178–1,823) were treated with increasing amounts of calf intestinal phosphatase followed by GST pull downs. Top, immunoblotting with α-HA; bottom, Coomassie staining.