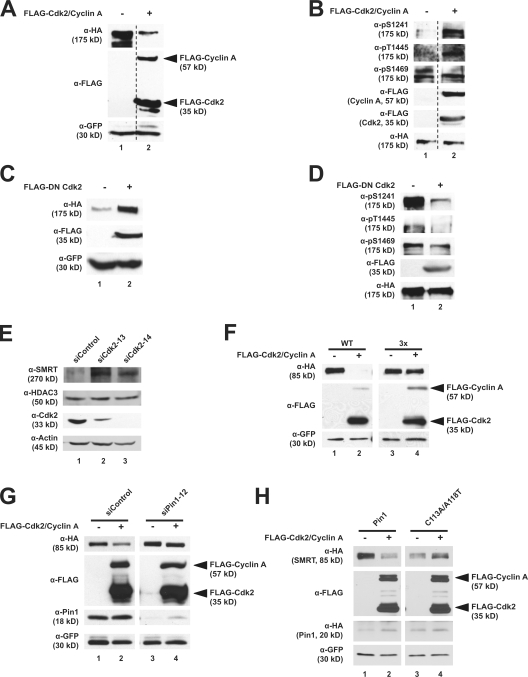
Figure 6.
Cdk2 stimulates SMRT phosphorylation in HeLa cells. (A) Coexpression of Cdk2 and cyclin A decreases SMRT steady-state levels. HeLa cells were cotransfected with HA-SMRT (1,012–2,507), GFP, FLAG-Cdk2, and FLAG–cyclin A as indicated. Unrelated lanes were removed. (B) Coexpression of Cdk2 and cyclin A increases SMRT phosphorylation. HeLa cells were transfected as in A and treated with 20 nM calyculin A for 1 h before harvest. Unrelated lanes were removed. (C) DN Cdk2 increases SMRT steady-state levels. HeLa cells were transfected with HA-SMRT (1,012–2,507), GFP, and FLAG-DN-Cdk2 (D145N), and WCEs were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (D) DN Cdk2 decreases SMRT phosphorylation. HeLa cells were transfected as in C and treated with 20 nM calyculin A 1 h before harvest. WCEs were subjected to immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. (E) siRNA-mediated knockdown of Cdk2 increases SMRT protein levels. Transfections were performed as in Fig. 2 D. (F) Cdk2 overexpression does not affect mutant SMRT protein levels. HeLa cells were cotransfected with HA-SMRT (1,188–1,833) 3× mutant, GFP, FLAG-Cdk2, and FLAG–cyclin A as indicated. (G) Endogenous Pin1 is required for Cdk2-mediated SMRT degradation. HeLa cells were cotransfected with HA-SMRT (1,188–1,833), GFP, FLAG-Cdk2, FLAG–cyclin A, and either siRNA-targeting Pin1 or control oligonucleotides as indicated. (H) Mutant Pin1 can block Cdk2-mediated SMRT degradation. HeLa cells were cotransfected with HA-SMRT (1,188–1,833), GFP, FLAG-Cdk2, FLAG–cyclin A, and either WT HA-Pin1 or the C113A/A118/T mutant as indicated. (A–H) WCEs were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.