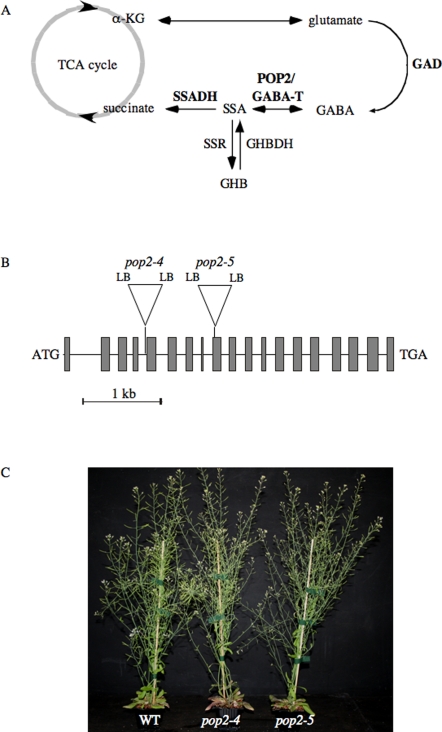
Figure 1. The GABA shunt metabolic pathway and the pop2 mutants.
(A) Schematic presentation of the GABA shunt metabolic pathway. The GABA shunt is composed of three enzymes (in bold). The cytosolic glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) catalyses the irreversible decarboxylation of glutamate to produce GABA. GABA is transported in the mitochondria to be converted into succinic semialdehyde (SSA) by a GABA transaminase (GABA-T/POP2). SSA is then oxidized by a succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH) to form succinate, which enters the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. In animals and possibly in plants, SSA can be converted into γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) by a SSA reductase (SSR) and GHB into SSA via another enzyme, the GHB dehydrogenase (GHBDH). α-KG; α-ketoglutarate. (B) Characterization of pop2-4 and pop2-5 T-DNA mutants. Gene structure of the GABA-T/POP2 (At3g22200) ORF and T-DNA insertions in both pop2-4 (SAIL_1230_C03) and pop2-5 (GABI_157D10) mutants. Exons are represented by boxes (drawn to scale). LB designs the left T-DNA borders. Junctions between the T-DNAs and the gene were sequenced. (C) Phenotype of the pop2-4 and pop2-5 mutants compared to WT (Col) plants. Seeds were sown on soil and grown for a total of 45 days in the greenhouse before being photographed.