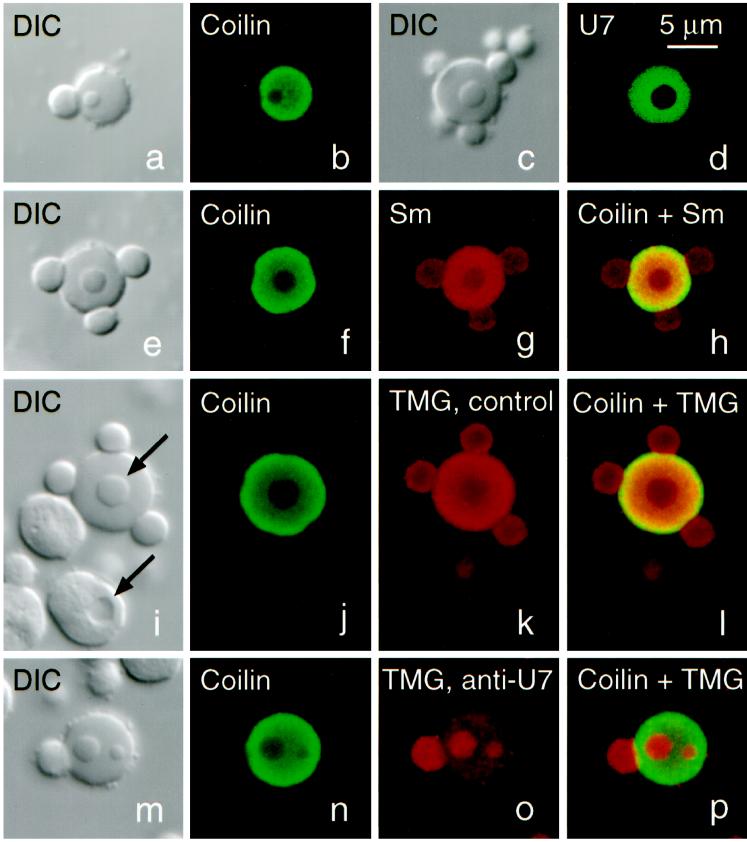
Figure 1.
Structure and composition of CBs from Xenopus oocytes (stages IV–VI). (a and b) DIC and immunofluorescence image of a CB stained for coilin (serum C236, fluorescein). Stain is limited to the matrix of the CB and is absent from the attached B-snurposome and the B-like inclusion. (c and d) DIC and fluorescence image of a CB from an oocyte injected 1 d previously with capped, fluorescein-labeled U7 snRNA, showing that U7, like coilin, is strictly limited to the matrix. (e–h) CB stained for coilin (serum C236, fluorescein) and Sm proteins (mAb Y12, Cy3). Overlap shows colocalization of coilin and Sm proteins in the matrix, only Sm proteins in the B-snurposomes and the inclusion. (i–l) CB stained for coilin (serum C236, fluorescein) and the trimethylguanosine (TMG) cap of snRNAs (mAb K121, Cy3). TMG occurs at highest concentration in the matrix but is also strong in the B-snurposomes and the inclusion. Upper arrow in the DIC image points to the inclusion in the CB; lower arrow points to a vacuole in a nucleolus. Note that the shadowing is on opposite sides, demonstrating that the inclusion in the CB is denser than the matrix in which it is embedded, whereas the vacuole is less dense than the body of the nucleolus. (m–p) CB stained exactly as in panels i–l, except that oocyte was injected 1 d previously with an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide against bases 1–16 of U7 snRNA. This treatment results in complete loss of U7 from the GV (Figure 2). Concomitantly, TMG stain in the matrix of the CB is reduced by ∼90% (compare o with k), but stain in the B-snurposome on the surface and the two inclusions is unaffected.