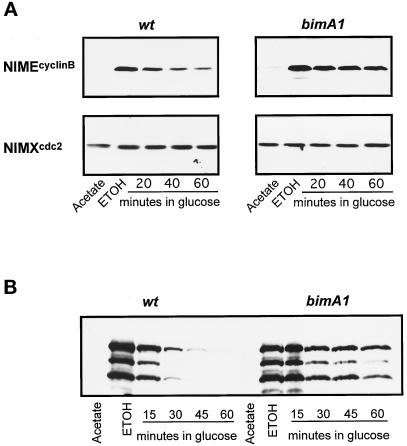
Figure 5.
APC/C-dependent stabilization of NIMEcyclinB and NIMA. (A) Cells of the wild-type (wt = R153) and bimA1APC3 cells containing a copy of alcA-driven nimEcyclinB were grown at 32°C to early log phase in acetate media (repressing for alcA). HU (100 mM) was added to the cells for 2 h to cause S phase arrest before rapid transfer to inducing medium (ethanol) also containing 100 mM HU but at 42°C. One hour after transfer to inducing medium at 42°C, glucose was added to repress expression from the alcA promoter. The abundance of NIMEcyclinB was determined by Western blotting. The same blots were also subsequently detected for p34cdc2 as loading control. (B) The experimental procedures for NIMA induction and repression in HU-arrested cells were as described in A by using a strain with alcA inducible nimA. NIMA was detected by Western blot after immunoprecipitation. No general proteolysis was observed in the samples from which NIMA was isolated, and the level of p34cdc2 was found by Western blotting to be constant. However, in addition to full-length NIMA (top band) numerous smaller NIMA degradation products were observed.