Abstract
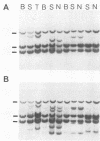
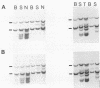
The DNA of lymphomas from 12 AKXD recombinant inbred mouse strains was analyzed to determine the presence of somatically acquired ecotropic and mink cell focus-forming proviruses. Mink cell focus-forming proviruses were associated primarily with T-cell lymphomas, whereas ecotropic proviruses were associated with lymphomas of B-cell and myeloid lineages. A model based on the results is proposed to explain the variation in lymphoma types observed in different AKXD strains.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buller R. S., Ahmed A., Portis J. L. Identification of two forms of an endogenous murine retroviral env gene linked to the Rmcf locus. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.29-34.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Cloyd M. W., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Cellular origin and role of mink cell focus-forming viruses in murine thymic lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):25–31. doi: 10.1038/295025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Structure of endogenous murine leukemia virus DNA in mouse genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5774–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Bedigian H. G., Thomas C. Y., Jenkins N. A. DNAs of two molecularly cloned endogenous ecotropic proviruses are poorly infectious in DNA transfection assays. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):437–444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.437-444.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Adams J. M., Dunn A. R., Cory S. Murine T lymphomas in which the cellular myc oncogene has been activated by retroviral insertion. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Adams J. M., Kemp D. J. Somatic rearrangements forming active immunoglobulin mu genes in B and T lymphoid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4943–4947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G., Quint W., Zijlstra M., Maandag E. R., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Melief C., Berns A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. The tandem direct repeats within the long terminal repeat of murine leukemia viruses are the primary determinant of their leukemogenic potential. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):945–952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.945-952.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A., Hobart M., Hengartner H., Rabbitts T. H. An immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene is altered in two T-cell clones. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):897–899. doi: 10.1038/286897a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham M., Adams J. M., Cory S. Murine T lymphomas with retroviral inserts in the chromosomal 15 locus for plasmacytoma variant translocations. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):740–743. doi: 10.1038/314740a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd A mouse gene on chromosome 5 that restricts infectivity of mink cell focus-forming recombinant murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):16–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gilbert W. Free and integrated recombinant murine leukemia virus DNAs appear in preleukemic thymuses of AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):155–162. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.155-162.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gilbert W. Somatically acquired recombinant murine leukemia proviruses in thymic leukemias of AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):70–82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.70-82.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Perlmutter A. P., Gilbert W. Monoclonal AKR/J thymic leukemias contain multiple JH immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7433–7436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoggan M. D., O'Neill R. R., Kozak C. A. Nonecotropic murine leukemia viruses in BALB/c and NFS/N mice: characterization of the BALB/c Bxv-1 provirus and the single NFS endogenous xenotrope. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):980–986. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.980-986.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto A., Adachi A., Sakai K., Matsuyama M. Long terminal repeat of Friend-MCF virus contains the sequence responsible for erythroid leukemia. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):30–42. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa Y., von Boehmer H., Haas W., Sakano H., Trauneker A., Tonegawa S. Identification of D segments of immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes and their rearrangement in T lymphocytes. Nature. 1981 Apr 16;290(5807):565–570. doi: 10.1038/290565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Viral integration near c-myc in 10-20% of mcf 247-induced AKR lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6808–6811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mucenski M. L., Taylor B. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. AKXD recombinant inbred strains: models for studying the molecular genetic basis of murine lymphomas. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4236–4243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quint W., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Cuypers T., Maandag E. R., Selten G., Berns A. Generation of AKR mink cell focus-forming viruses: a conserved single-copy xenotrope-like provirus provides recombinant long terminal repeat sequences. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):432–438. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.432-438.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A., Lenz J., Ruprecht R., Cloyd M. W. Tissue selectivity of murine leukemia virus infection is determined by long terminal repeat sequences. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):862–866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.862-866.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovigatti U., Mirro J., Kitchingman G., Dahl G., Ochs J., Murphy S., Stass S. Heavy chain immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in acute nonlymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1984 May;63(5):1023–1027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W. Status of the association of mink cell focus-forming viruses with leukemogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1265–1268. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pincus T. Quantitative studies of naturally occurring murine leukemia virus infection of AKR mice. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):429–436. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Zijlstra M., Melief C., Berns A. Involvement of c-myc in MuLV-induced T cell lymphomas in mice: frequency and mechanisms of activation. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3215–3222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. Y., Boykin B. J., Famulari N. G., Coppola M. A. Association of recombinant murine leukemia viruses of the class II genotype with spontaneous lymphomas in CWD mice. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):314–323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.314-323.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. Y., Coffin J. M. Genetic alterations of RNA leukemia viruses associated with the development of spontaneous thymic leukemia in AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):416–426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.416-426.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich K., Nexø B. A. Spontaneous expression of C-type virus in DBA/2 mice is associated with an increased rate of mortality, independent of neoplastic disease. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):273–278. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.273-278.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt M., Haggblom C., Swift S., Haas M. Envelope gene and long terminal repeat determine the different biological properties of Rauscher, Friend, and Moloney mink cell focus-inducing viruses. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):184–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.184-192.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra M., Quint W., Cuypers T., Radaszkiewicz T., Schoenmakers H., de Goede R., Melief C. Ecotropic and mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia viruses integrate in mouse T, B, and non-T/non-B cell lymphoma DNA. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1037–1047. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1037-1047.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]