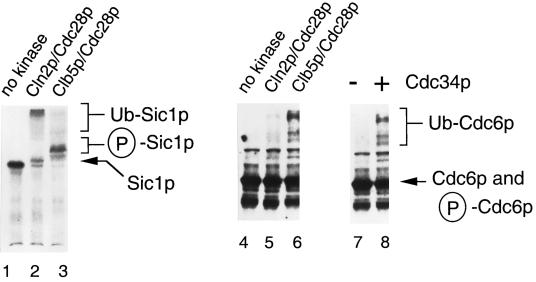
Figure 4.
In vitro ubiquitination of Cdc6p depends on Clbp/Cdc28p and Cdc34p. Lanes 1–6, Clb5p/Cdc28p dependence of Cdc6p ubiquitination. Lanes 1–3, ubiquitination of Sic1p was carried out as previously described (Verma et al., 1997c). Lanes 1–3, in vitro ubiquitination assays with 35S-labeled Sic1p, produced by in vitro translation. All reactions contained DEAE-fractionated extract of G1-arrested RJD885 cells, purified Cdc34p, an ATP-regenerating system, salts, and ubiquitin. Lane 1, no kinase added; lane 2, insect cell lysate containing Clnp2/Cdc28p was added; lane 3, insect cell lysate containing Clb5p/Cdc28p was added. Incubations were carried out for 1 h at 25°C, treated with 20 μg/ml RNase A for 15 min at 37°C to remove RNA–protein adducts, and quenched with SDS-PAGE loading buffer. Reactions were electrophoresed, and the gel was dried and autoradiographed for 17 h. Bands correspond-ing to Sic1p, phosphorylated Sic1p, and ubiquitinated Sic1p are indicated and were identified based on previous descriptions (Feldman et al., 1997). Lanes 4–6, ubiquitination of Cdc6p. Reactions are exactly as described for lanes 1–3, respectively, except that in vitro-translated Cdc6-Myc9p was not labeled with 35S. After electrophoresing, proteins were blotted to Hybond nitrocellulose and probed with monoclonal anti-Myc antibody 9E10. Westerns were developed with the Super Signal luminescent reagent (Pierce, Rockford, IL). Lanes 7 and 8, Cdc34p dependence of Cdc6p ubiquitination. All reactions contained DEAE-fractionated extract of G1 arrested RJD885 cells, insect cell lysate containing Clb5p/Cdc28p, an ATP-regenerating system, salts, and ubiquitin. Purified Cdc34p was added (lane 8) or omitted (lane 7). Samples were processed exactly as described for the samples shown in lanes 4–6.