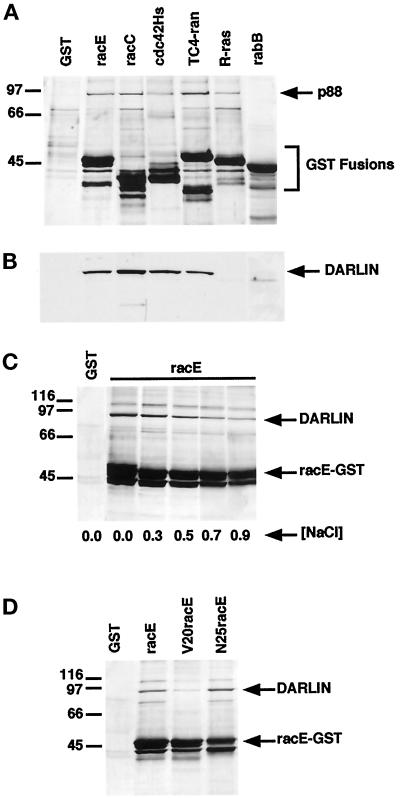
Figure 1.
Identification of darlin as a small GTPase-binding protein from Dictyostelium. (A) Isolation of Dictyostelium proteins that bind to small GTPases. In bacteria we expressed GST and GST fusion proteins of Dictyostelium racE, racC, and rabB, and human cdc42Hs, TC4-ran, and R-ras. The different GST fusion proteins were incubated with Dictyostelium lysates and washed, and the proteins were eluted off the beads. The eluted proteins were subsequently analyzed by SDS-PAGE and visualized by silver staining. A protein of ∼88 kDa bound to all GST fusion proteins except that for rabB or to GST alone. GST migrates below the area shown. (B) Darlin binds to a subset of small GTPases. Western blot analysis of the same samples shown in A using a polyclonal antibody against the purified darlin protein. Darlin bound to the GST fusion proteins for racE, racC, cdc42Hs, and TC4-ran but not to those for R-ras or rabB. Note that the 88-kDa protein that bound to R-ras (A) did not react with the anti-darlin antibody. (C) Darlin binds to racE under high ionic strength. The racE–GST fusion protein was incubated with Dictyostelium lysates in a range of NaCl concentrations and analyzed as in A. Darlin binds to racE even under high ionic strength buffer conditions. (D) Darlin binds preferentially to the GDP-bound form of racE. GST and GST fusion proteins of racE, the constitutively GTP-bound V20RacE, and the constitutively GDP-bound N25racE were incubated with Dictyostelium lysates in 0.4 M NaCl and analyzed as in A.