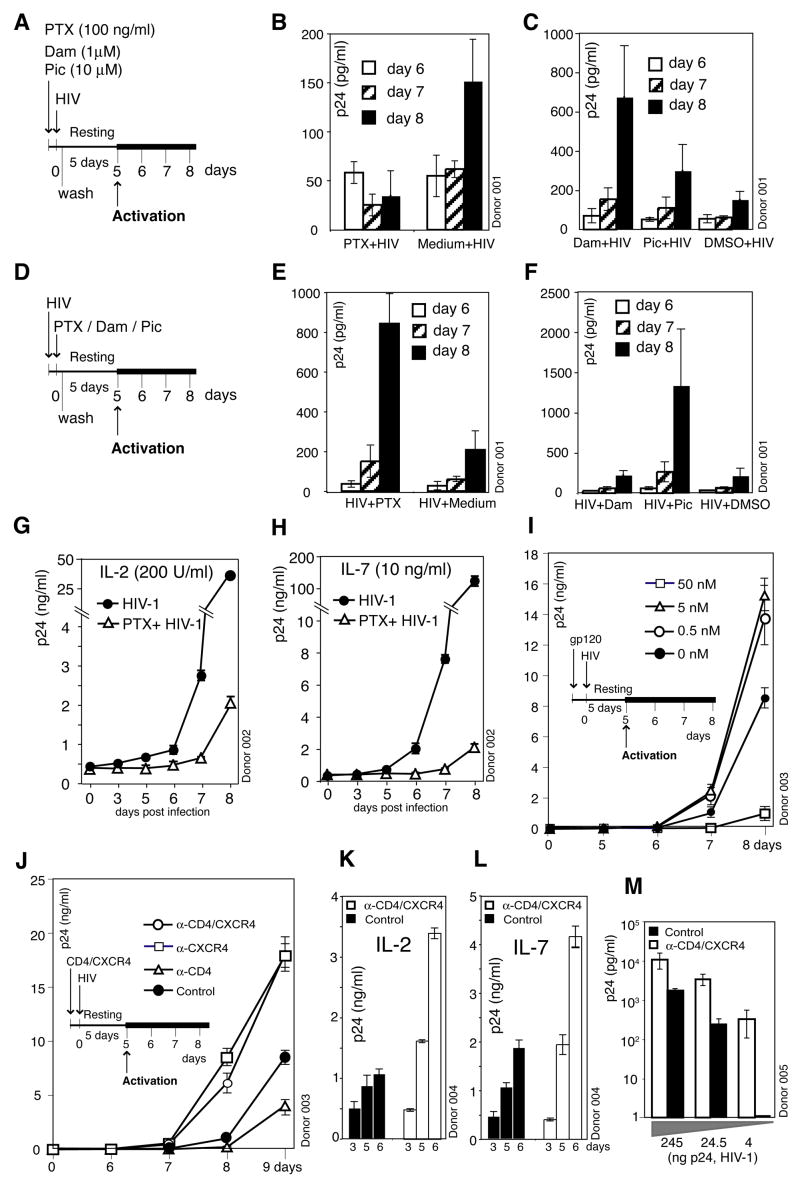
Figure 1. Requirement of CXCR4 Signaling for HIV Infection of Resting CD4T Cells.
(A to H) Inhibition of HIV infection by pertussis toxin (PTX). Cells were treated with PTX, damnacanthal (Dam), piceatannol (Pic), or medium, DMSO for controls, infected, washed, cultured for 5 days, and then activated with anti-CD3/CD28 beads (A). Shown is viral replication measured by p24 release (B, C). For comparison, cells were infected first, treated with these reagents, washed, and then cultured and activated as above (E, F). (G and H) Cells were also cultured in IL-2 or IL-7 for 4 days, treated with PTX, infected, cultured with cytokines, and then activated as above. (I) Enhancement of HIV infection by gp120. Cells were pre-stimulated with gp120IIIB, infected, incubated and then activated. (J) Enhancement of HIV infection by anti-CD4/CXCR4 beads. Cells were pre-stimulated with anti-CD4/CXCR4, anti-CD4, or anti-CXCR4 beads, infected, incubated and then activated. (K and L) Enhancement of HIV replication by anti-CD4/CXCR4 beads in cytokine-stimulated cells. Cells were cultured in IL-2 or IL-7 for 4 days, pre-stimulated with anti-CD4/CXCR4 beads, infected, washed, and then cultured in cytokines. (M) HIV dosage-dependent enhancement of viral infection by anti-CD4/CXC4 beads. Cells were pre-stimulated with anti-CD4/CXCR4 beads, infected, washed, incubated, and then activated.