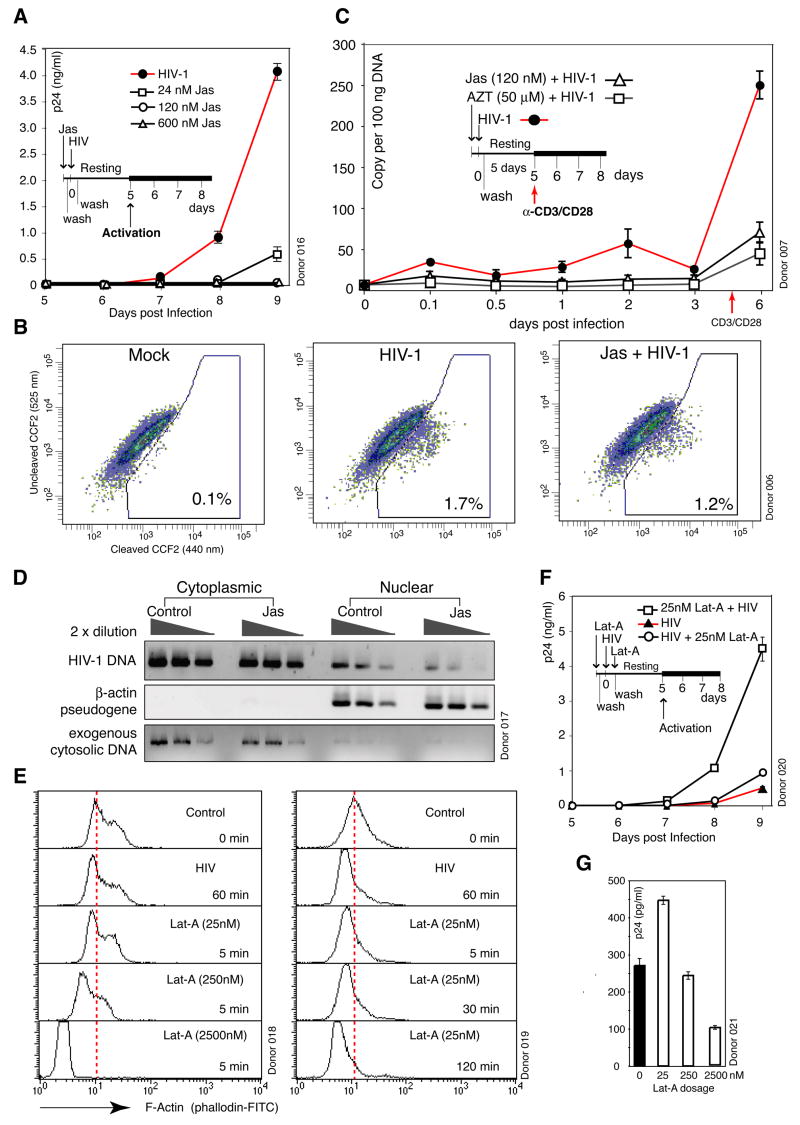
Figure 4. Viral Requirement for Actin Activity in HIV Infection of Resting CD4 T Cells.
(A) Jas inhibition of HIV infection. Cells were treated with Jas for 2 hours, washed, infected, washed, cultured, and then activated with anti-CD3/CD28 beads to initiate viral replication. (B) Effects of Jas on viral fusion. Cells were treated with 120 nM Jas, infected with HIV(BlaM-Vpr), washed, and then loaded with CCF2 for measuring fusion. (C) Effects of Jas on viral DNA synthesis. Cells were treated with 120 nM Jas for 1 hour and infected. Viral DNA synthesis was measured by real-time PCR. AZT was used as a control. (D) Inhibition of viral DNA nuclear localization by 120 nM Jas. Cells were treated with 120 nM Jas, infected, washed, lysed, and then fractionated into cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions as in Figure 2C. (E) Dosage and time-dependent actin depolymerization by Lat-A. Cells were treated with Lat-A for 5 min (left panel), or with 25 nM Lat-A for various times (right panel), and stained with FITC-phalloidin for flow cytometry. Untreated and HIV-infected cells were used as controls. (F) Enhancement of HIV infection by Lat-A. Cells were treated with 25 nM Lat-A for 5 minutes, washed, infected, washed, cultured, and then activated. As a control, cells were also infected first, washed, treated with Lat-A for 5 minutes, washed, and then incubated and activated identically. (G) Dosage-dependent effects of Lat-A on HIV infection. Cells were treated with Lat-A for 5 min at different dosages, infected, washed, incubated, and then activated.