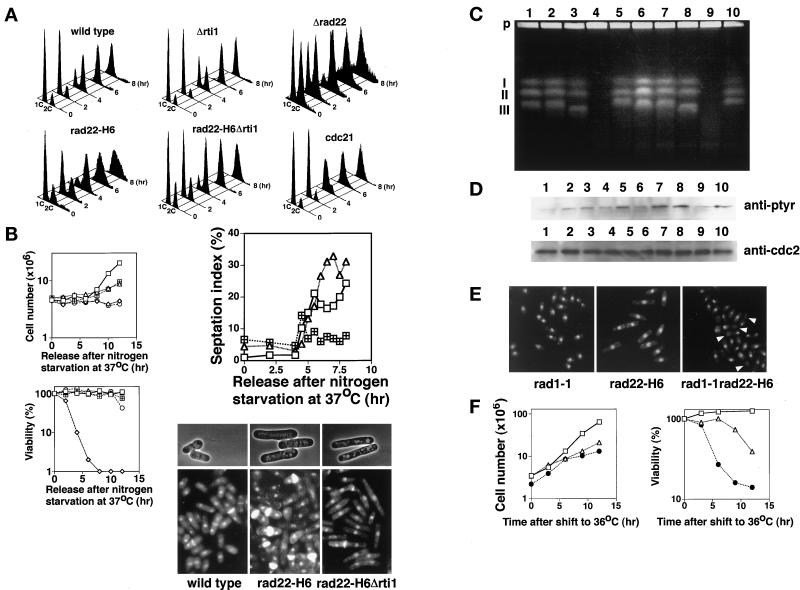
Figure 3.
Cells defective in rad22+/rti1+ are not delayed in bulk DNA synthesis but arrest before G2 phase. (A) Flow cytometry of rad22 and rti1 mutants released from G1. Wild-type, Δrad22 (HM367), Δrti1(HM368), rad22-H6 (HM366), rad22-H6 Δrti1 (HM369), and cdc21-M63 (HM128) cells were grown in PM + leu medium to middle log phase at 23°C. Each strain was incubated in nitrogen-free PM medium containing leucine (50 μg/ml) at 23°C for 24 h and then at 37°C for 12 h. The cells were transferred to PM + leu medium at 37°C for starting cell cycling. Incubation was continued at 37°C for the indicated times. (B) Proliferation, viability, and septation of rad22/rti1 mutant cells released from G1 at 37°C. Wild-type (square), rad22-H6 (triangle), rad22-H6 Δrti1 (square with plus), cdc21-M63 (diamond), and cdc25–22 (circle) cells were incubated as described in A, and their cell number and viability were determined. Septation indexes were determined after double staining with DAPI and calcofluor (Alfa et al., 1993). For photographs, cells at 8 h were fixed with 70% ethanol, and some were stained with DAPI and calcofluor. (C) Pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Wild-type (lanes 1 and 6), rad22-H6 (lanes 2 and 7), rad22-H6 Δrti1(lanes 3 and 8), cdc21-M63 (lanes 4 and 9), and cdc25–22 (lane 5 and 10) cells were collected at 6 h (lanes 1–5) and 8 h (lanes 6–10), and their chromosomal DNA was prepared in agarose plugs and separated by pulsed field gel electrophoresis as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. P, agarose plug at the origin of electrophoresis; I–III, positions of S. pombe chromosomes 1–3, respectively. (D) Levels of tyrosine-phosphorylated Cdc2 in rad22/rti1 mutant cells at the stage of post-DNA synthesis. Wild-type (lanes 1 and 6), rad22-H6 (lanes 2 and 7), rad22-H6 Δrti1 (lanes 3 and 8), cdc21-M63 (lanes 4 and 9) and cdc25–22 (lanes 5 and 10) cells were collected at 6 h (lanes 1–5) and 8 h (lanes 6–10). Cell extracts were prepared and electrophoresed on 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gels with loading of 60 μg of protein per lane for the detection of tyrosine-phosphorylated Cdc2 (upper lanes) and 15 μg of protein per lane for the detection of Cdc2 (lower lanes), transferred to nitrocellulose membranes, and probed with anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (purchased from NBL) and anti-Cdc2 antibody, respectively. The anti-Cdc2 rabbit antibody was raised against the C-terminal seven amino acids of S. pombe Cdc2 protein. (E) When combined with the checkpoint rad1-1 mutation, rad22-H6 cells enter premature mitosis. Rapidly growing rad1-1(HM73), rad22-H6, and rad22-H6 rad1-1 (HM105) cells were incubated in YE at 36°C for 12 h. Arrows show cut cells, those in typical premature mitosis. (F) Proliferation and viability of rad22-H6 rad1-1 cells. Rapidly growing rad1-1 (MH73; square), rad22-H6 (HM366; triangle), and rad22-H6 rad1-1 (MH105; filled circle) cells were incubated in YE at 36°C for various times, and the cell number and viability were determined.