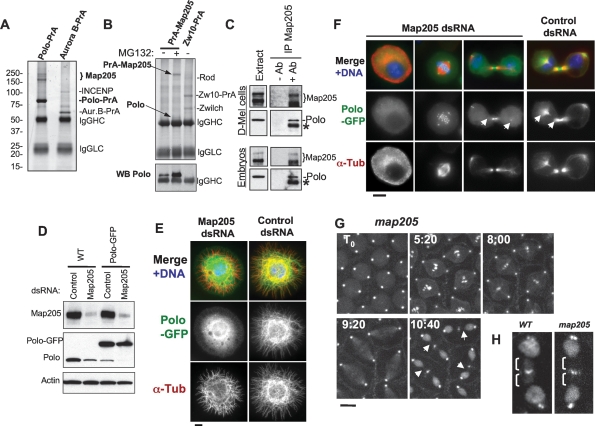
Figure 2.
Polo interacts with Map205, and this is required for its localization to MTs. (A) Polo specifically interacts with Map205. Polo-PrA and Aurora B-PrA (control) were purified from stably expressing cell lines, and purified proteins were resolved on SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue. The indicated proteins were identified by mass spectrometry. (IgGHC) IgG heavy chain; (IgHLC) IgG light chain. (Left) Molecular mass markers are in kilodaltons (kDa). (B) Reciprocal purification. (Top) PrA-Map205 and Zw10-PrA (control) were purified from stably expressing cell lines, and products were analyzed as in A. In one sample, cells were treated overnight with 25 μM MG132 to inhibit the proteasome, which results in a stabilization of Map205 (but does not lead to an arrest of the majority of the cells in mitosis). (Bottom) The same purification products were probed for Polo by Western blot. (C) Endogenous Polo and Map205 interact in D-Mel cells and embryos. Polo was coimmunoprecipitated with Map205 using anti-Map205 antibodies from D-Mel cells and from syncytial embryos. As a control, antibodies were not added. (*) Antibodies from the IP cross-reacting in the Polo Western blot. (D) Depletion of Map205 by RNAi. D-Mel cells, wild-type or stably expressing Polo-GFP, were treated with dsRNA against Map205 or the bacterial kanamycin-resistance gene (control). Four days later, cells were analyzed by Western blotting against Map205, Polo, and actin (loading control). Note that in addition to the depletion of Map205, Polo levels are also reduced. (E,F) Polo requires Map205 for its localization to MTs. (E) Polo-GFP cells were treated with Map205 dsRNA or control dsRNA (as in D), spread on concanavalin-A, fixed with methanol/formaldehyde, and stained for α-tubulin (red) GFP (anti-GFP; green), and DNA (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (F) Polo-GFP cells were treated with Map205 or control dsRNA (as in D and E), fixed with formaldehyde, and stained for α-tubulin (red) and DNA (blue). (Right) Note that unlike in the control, Polo-GFP fails to colocalize with MTs in cytokinesis after Map205 RNAi (arrows). Also compare with cells in Figure 1B. Bar, 5 μm. (G) GFP-Polo dynamics in a transgenic syncytial embryo laid by a map205 homozygous null mother (cycle 13) by time lapse (time is shown in minutes:seconds). Note that, unlike in map205+ embryos (Fig. 1D), GFP-Polo fails to localize to the MTs of the central spindle during karyokinesis in map205-null embryos (arrows). Bar, 10 μm. (H) Magnified view of karyokinetic nuclei from wild-type (WT) or map205-null embryos expressing GFP-Polo (taken from G and Fig. 1D). Note that unlike in the wild-type control, GFP-Polo fails to localize to central spindle MTs in the map205-null embryo.