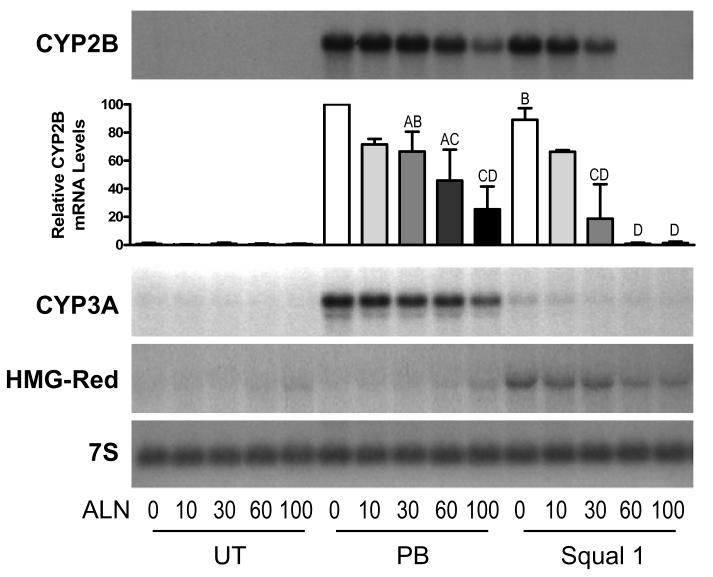
Fig. 3.
Concentration-dependent effects of alendronate treatment on squalestatin 1- and phenobarbital-inducible CYP2B, CYP3A and HMG-CoA reductase mRNA levels in primary cultured rat hepatocytes. At 48 hr after plating, primary cultured rat hepatocytes were incubated for 48 hr in medium alone (UT) or containing 100 μM phenobarbital (PB) or 0.1 μM squalestatin 1 (Squal 1), alone (0) or in combination with 10, 30, 60 or 100 μM alendronate (ALN). After treatment, hepatocytes were harvested for measurement of CYP2B, CYP3A or HMG-CoA reductase (HMG-Red) mRNA levels by northern blot hybridization. Individual panels show autoradiographs from a representative experiment; also shown is an autoradiograph from the CYP2B blot that had been hybridized with 7S cDNA probe, to demonstrate consistency of RNA loading and transfer among samples. Also shown is a graphical representation of the densitometrically quantified CYP2B mRNA content data from three independent hepatocyte preparations (except for the 10 μM ALN values, which are from two preparations). Each bar represents the mean ± sd CYP2B mRNA content as a percentage of the group treated with PB alone (PB, 0), except for the PB, 0 group itself (defined as 100% in each experiment) and the 10 μM ALN groups (presented as mean ± range). Groups not sharing a letter are significantly different from each other, p<0.05.